Euclidean Geometry Cheat Sheet
Struggling to remember the exact wording for geometry proofs? This tool is designed to help HKDSE Mathematics students instantly find and review geometry reasons covered in the syllabus.
Lines
adj. $\angle$s on st. line
adj. $\angle$s on st. line
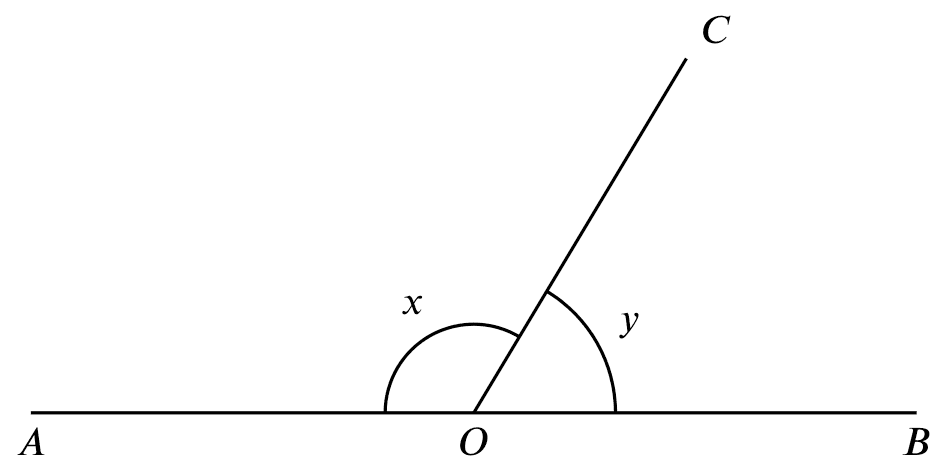
If
If AOB is a straight line,
Then
$x+y=180^{\circ}$
adj. $\angle$s supp.
adj. $\angle$s supp.
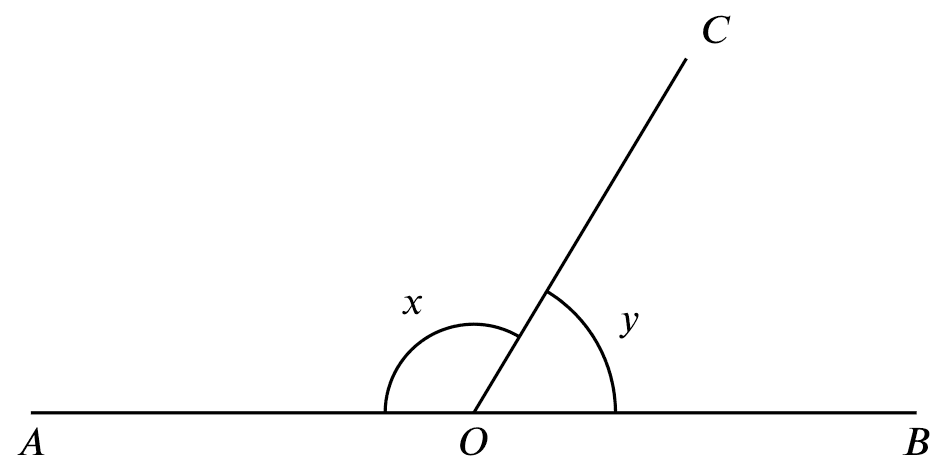
If
If $x+y=180^{\circ}$
Then
AOB is a straight line.
$\angle$s at a pt.
$\angle$s at a pt.
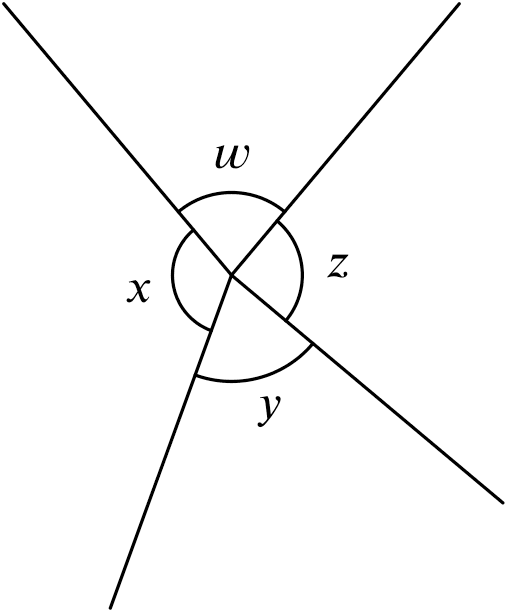
$w+x+y+z=360^{\circ}$
vert. opp. $\angle$s
vert. opp. $\angle$s
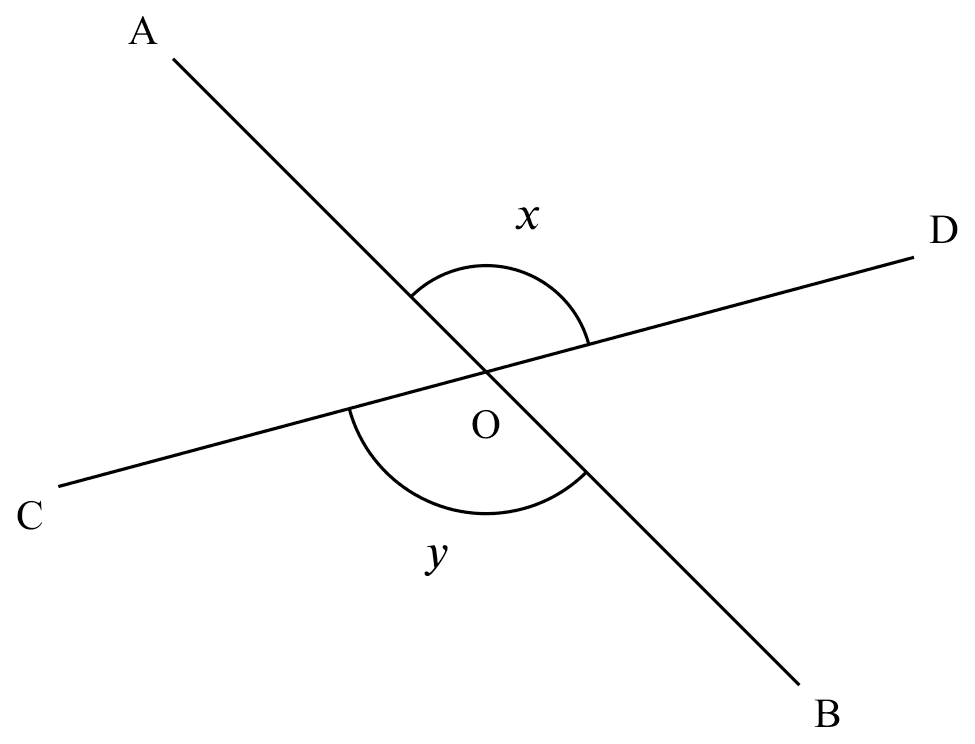
If
If lines AB and CD meet at O,
Then
$x = y$
corr. $\angle$s, AB$\parallel$CD
corr. $\angle$s, AB$\parallel$CD
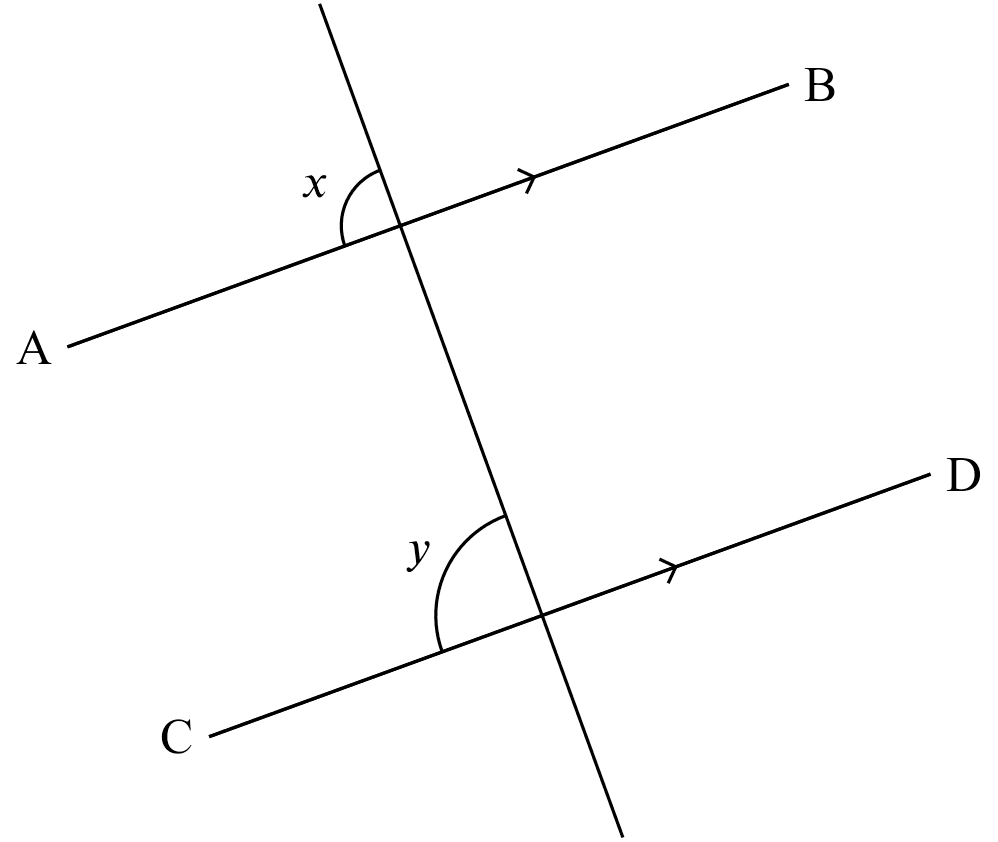
If
If $AB \parallel CD$,
Then
$x = y$
alt. $\angle$s, AB$\parallel$CD
alt. $\angle$s, AB$\parallel$CD
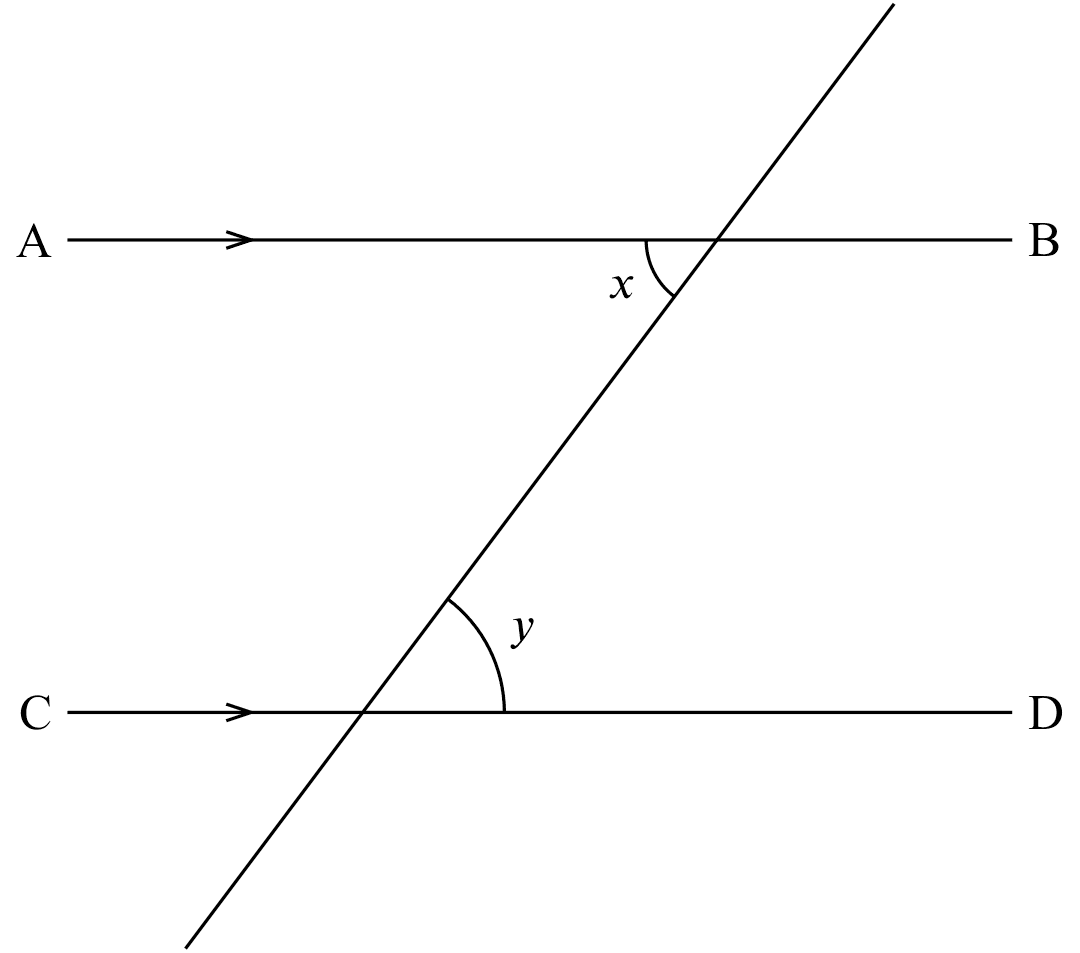
If
If $AB \parallel CD$,
Then
$x = y$
int. $\angle$s, AB$\parallel$CD
int. $\angle$s, AB$\parallel$CD
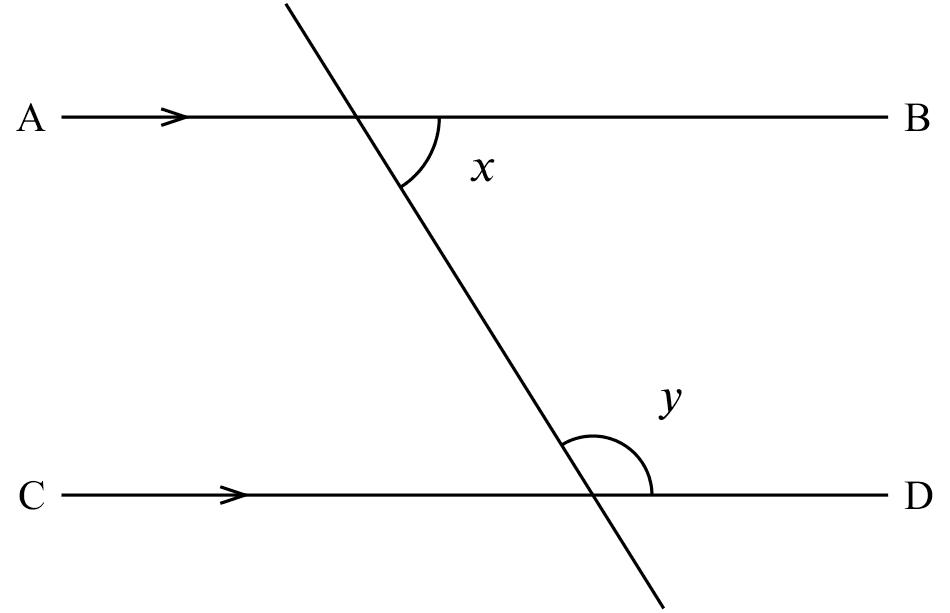
If
If $AB \parallel CD$,
Then
$x+y=180^{\circ}$
corr. $\angle$s equal
corr. $\angle$s equal
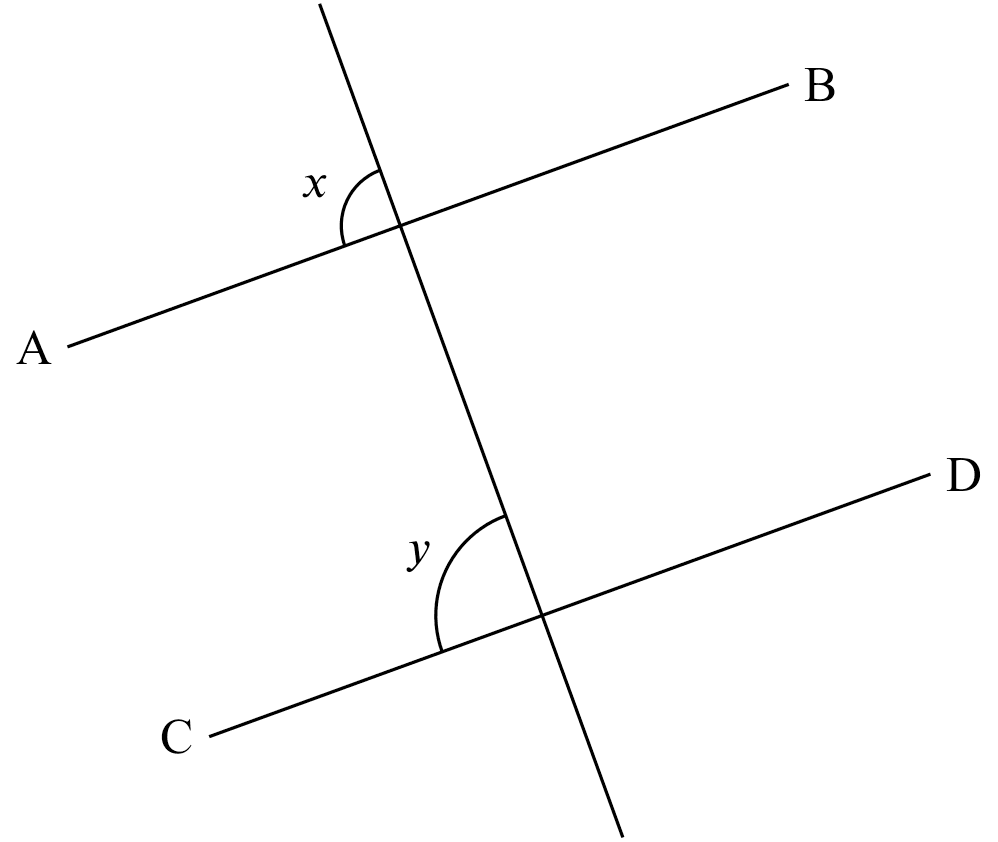
If
If $x = y$,
Then
$AB \parallel CD$
alt. $\angle$s equal
alt. $\angle$s equal
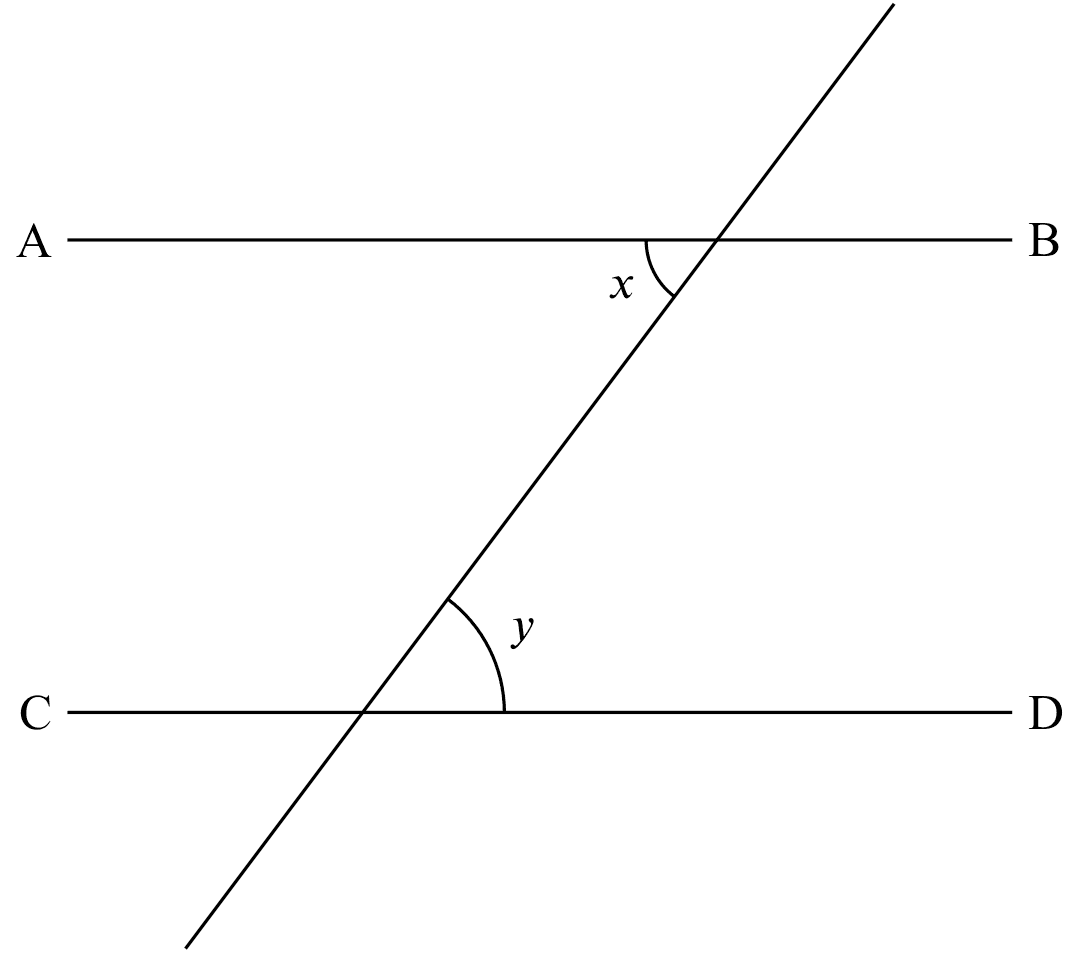
If
If $x = y$,
Then
$AB \parallel CD$
int. $\angle$s supp.
int. $\angle$s supp.
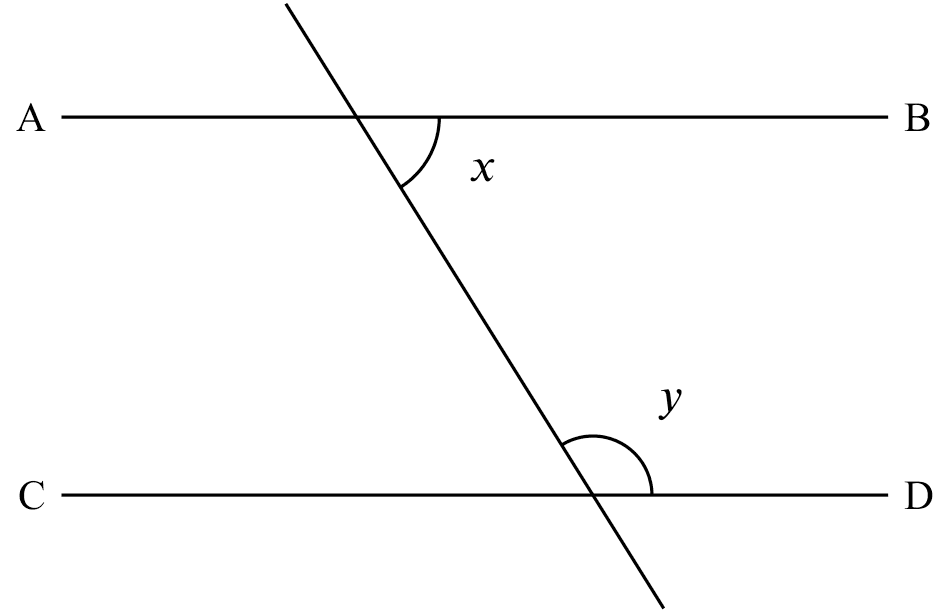
If
If $x+y=180^{\circ}$
Then
$AB \parallel CD$
mid-pt. theorem
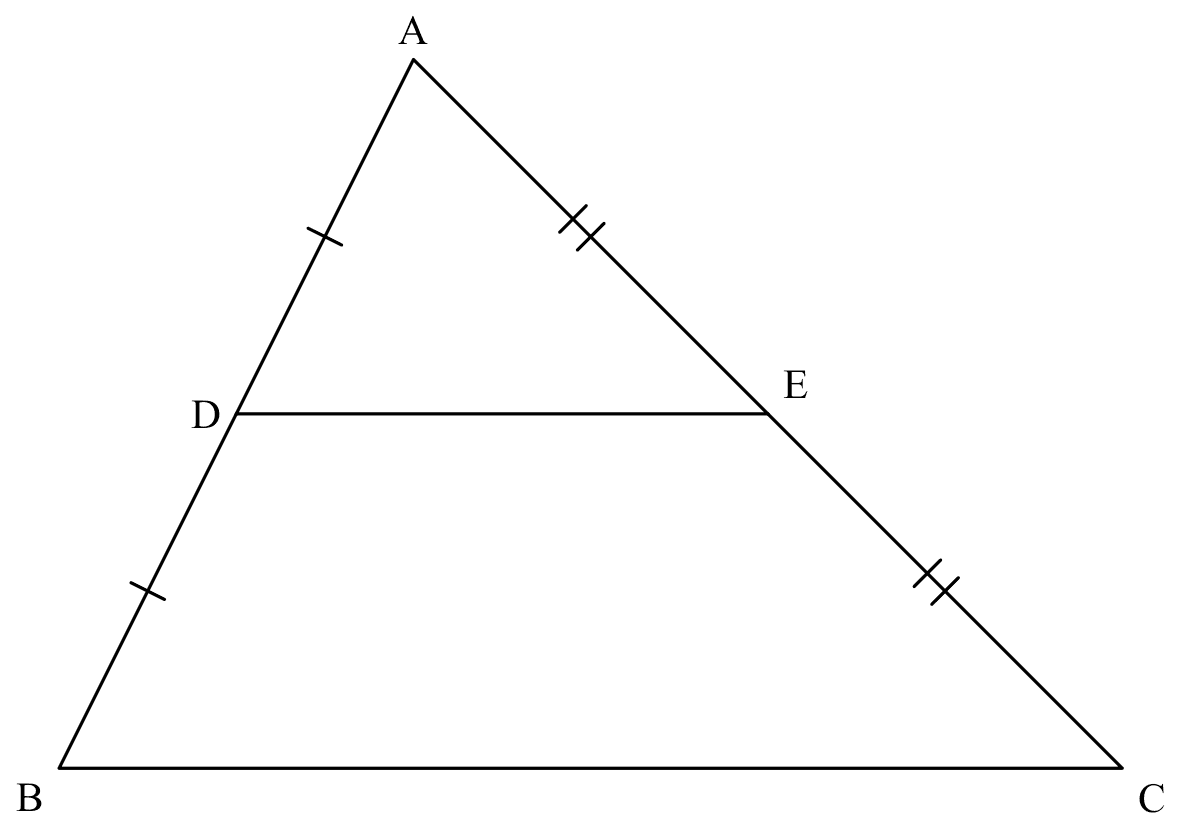
If
If $AD=DB$ and $AE=EC$ (D,E midpoints of AB, AC),
Then
$DE \parallel BC$
$BC = 2DE$
intercept theorem
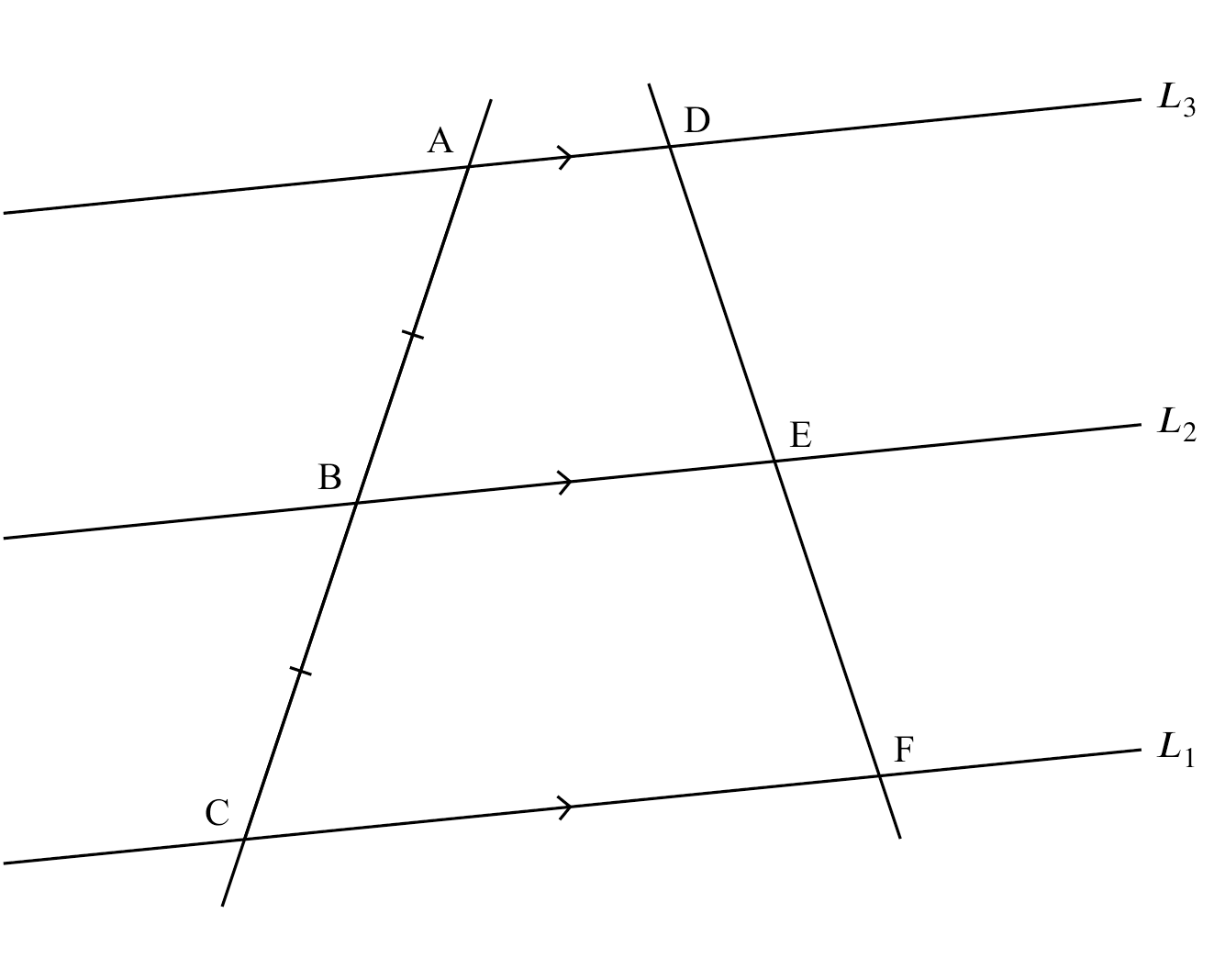
If
If $AD \parallel BE \parallel CF$ and $AB = BC$,
Then
$DE = EF$
Triangles
$\angle$ sum of $\triangle$
$\angle$ sum of $\triangle$
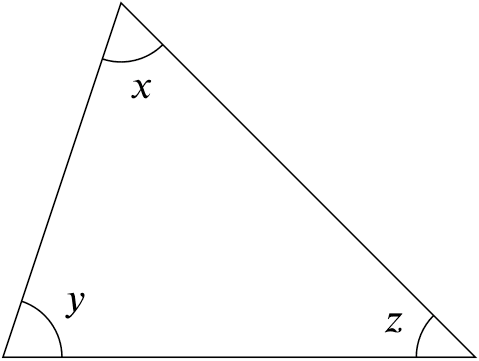
$x+y+z=180^{\circ}$
ext. $\angle$ of $\triangle$
ext. $\angle$ of $\triangle$
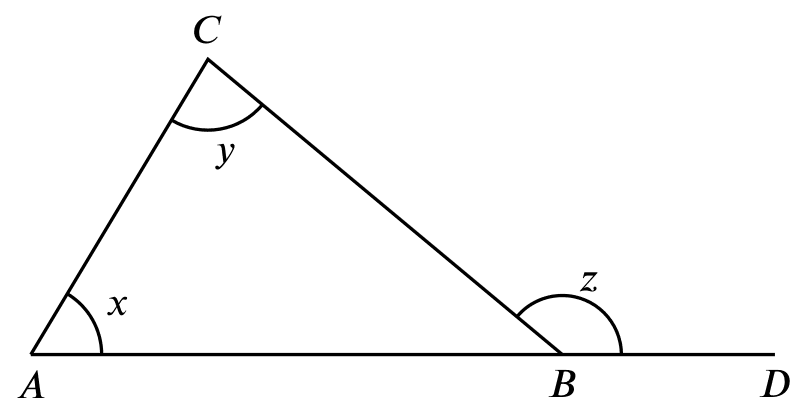
$x+y=z$
SAS
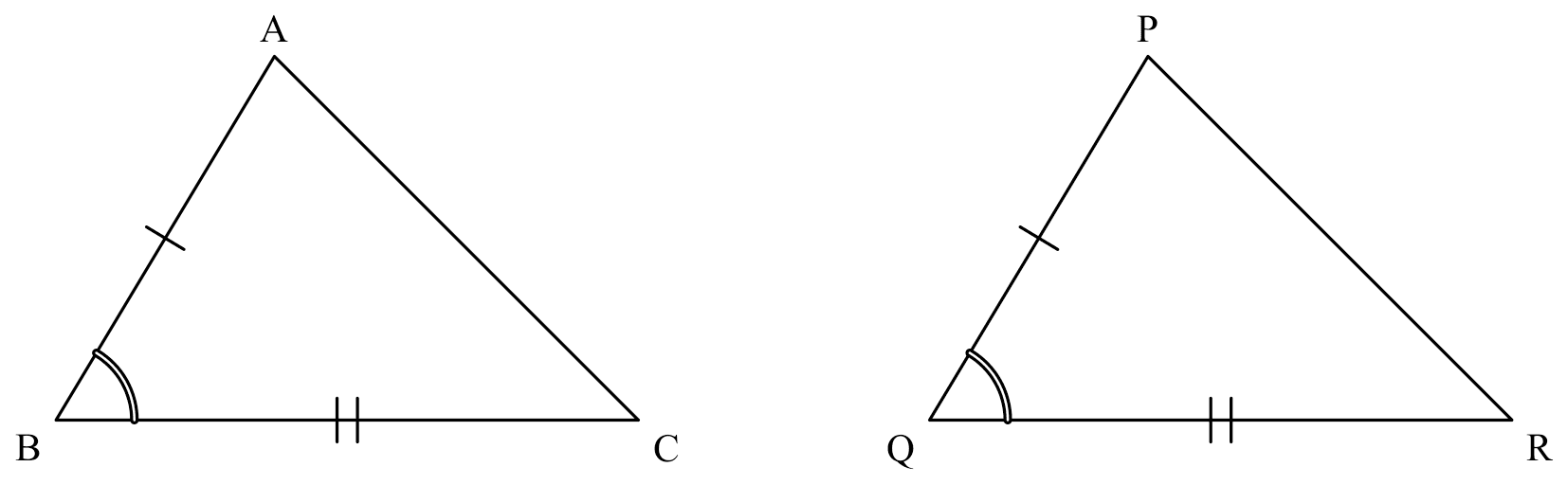
If
If $AB=PQ$, $\angle ABC=\angle PQR$, $BC=QR$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$
SSS
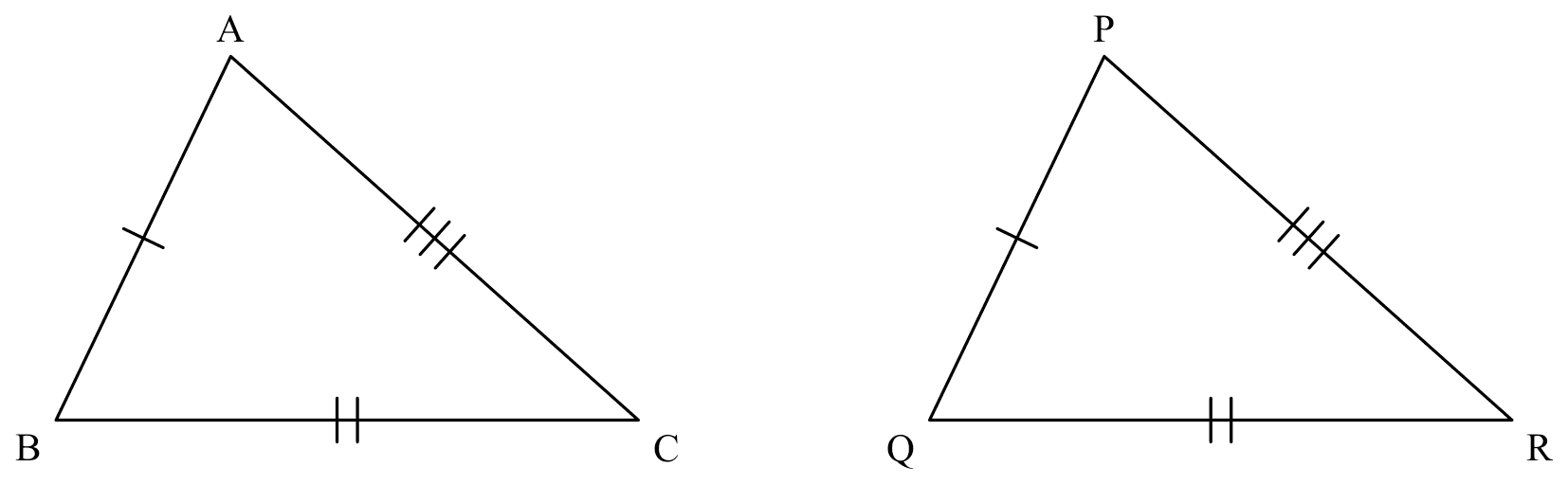
If
If $AB=PQ$, $BC=QR$, $AC=PR$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$
ASA
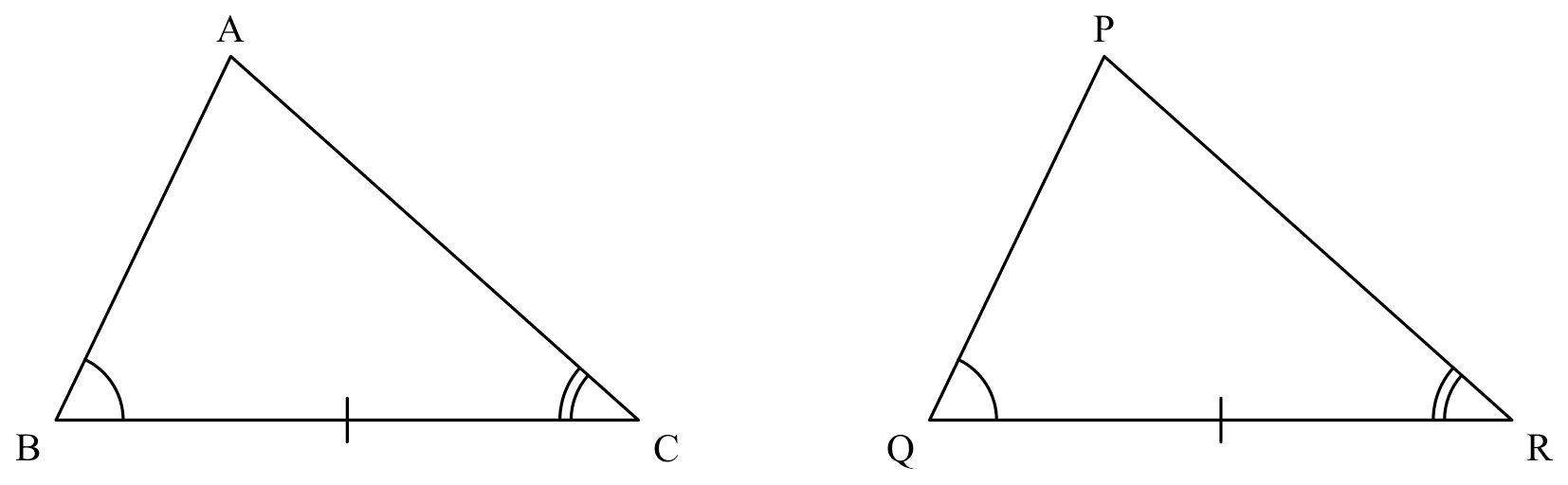
If
If $\angle ABC=\angle PQR$, $BC=QR$, $\angle ACB=\angle PRQ$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$
AAS
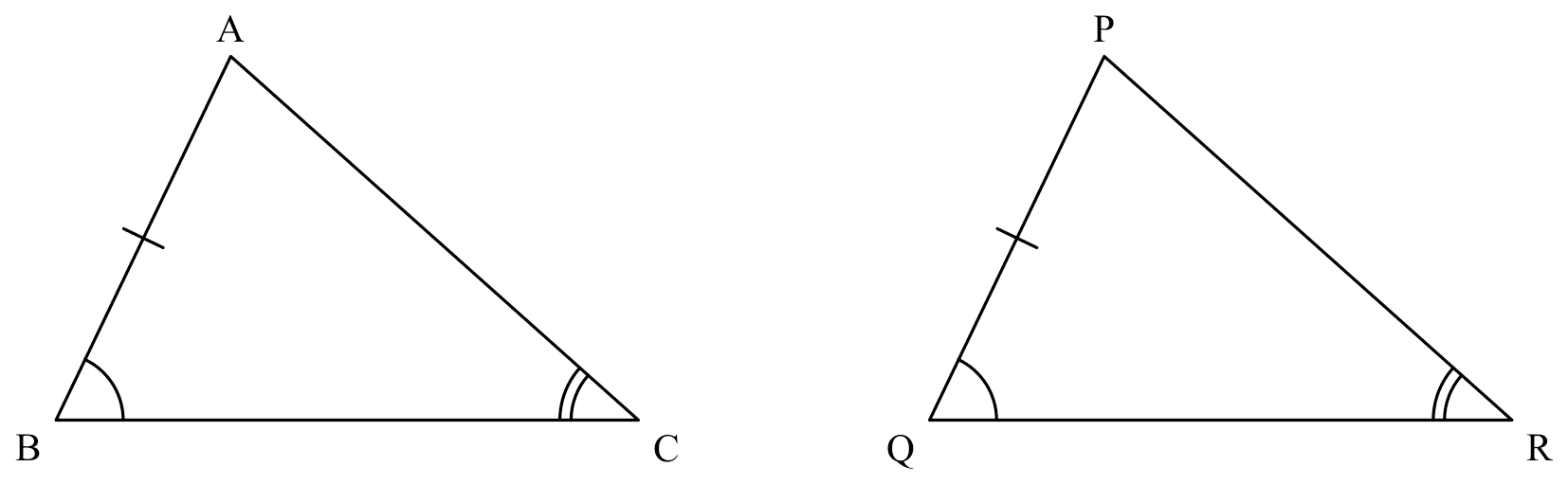
If
If $\angle ABC=\angle PQR$, $\angle ACB=\angle PRQ$, $AB=PQ$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$
RHS
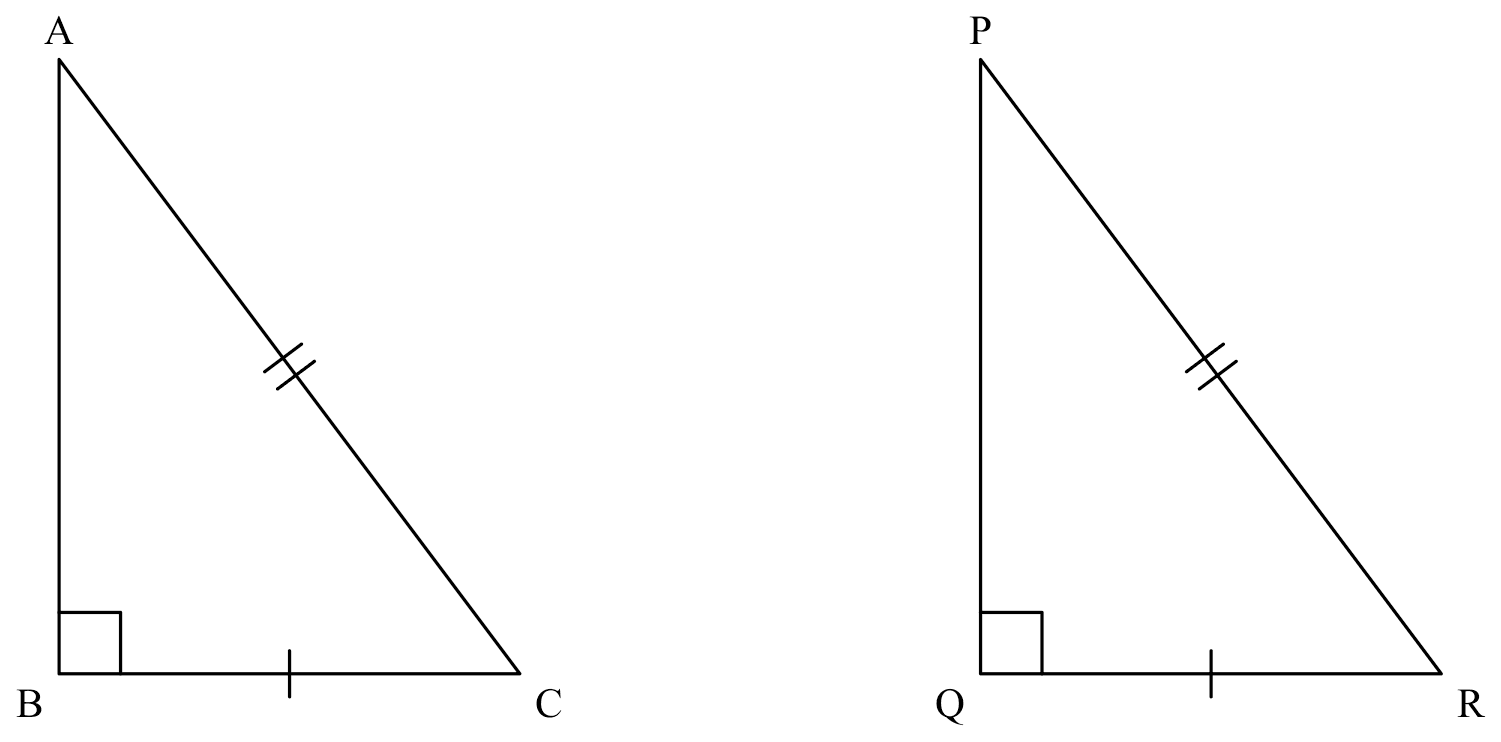
If
If $\angle ABC=\angle PQR=90^{\circ}$, $AC=PR$ (hypotenuse), $BC=QR$ (side),
Then
$\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$
AAA
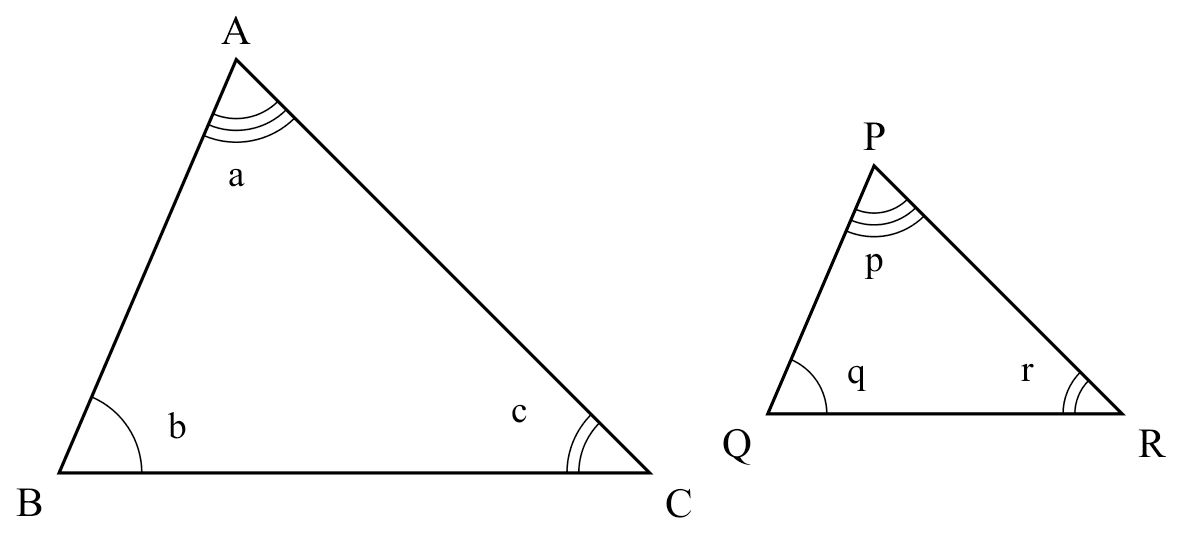
If
If $a=p$, $b=q$, $c=r$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$
AA
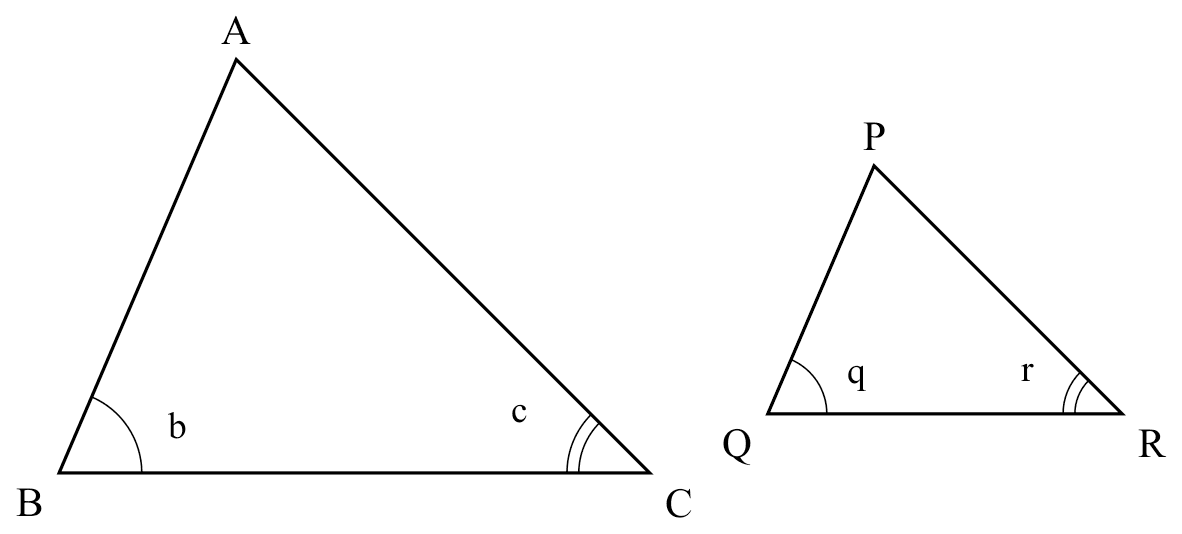
If
If $b=q$, $c=r$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \sim \triangle PQR$
3 sides proportional
If
If $\frac{AB}{PQ}= \frac{BC}{QR}= \frac{AC}{PR}$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \sim \triangle PQR$
ratio of 2 sides, inc. $\angle$
ratio of 2 sides, inc. $\angle$
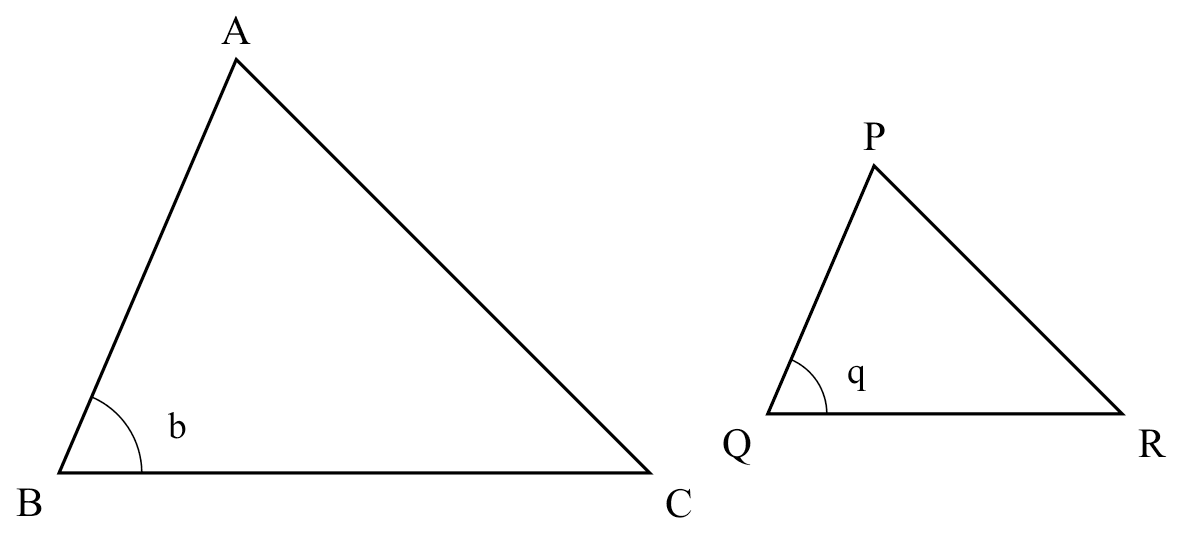
If
If $b=q$ and $\frac{AB}{PQ}= \frac{BC}{QR}$,
Then
$\triangle ABC \sim \triangle PQR$
corr. $\angle$s, $\cong$ $\triangle$s
corr. $\angle$s, $\cong$ $\triangle$s
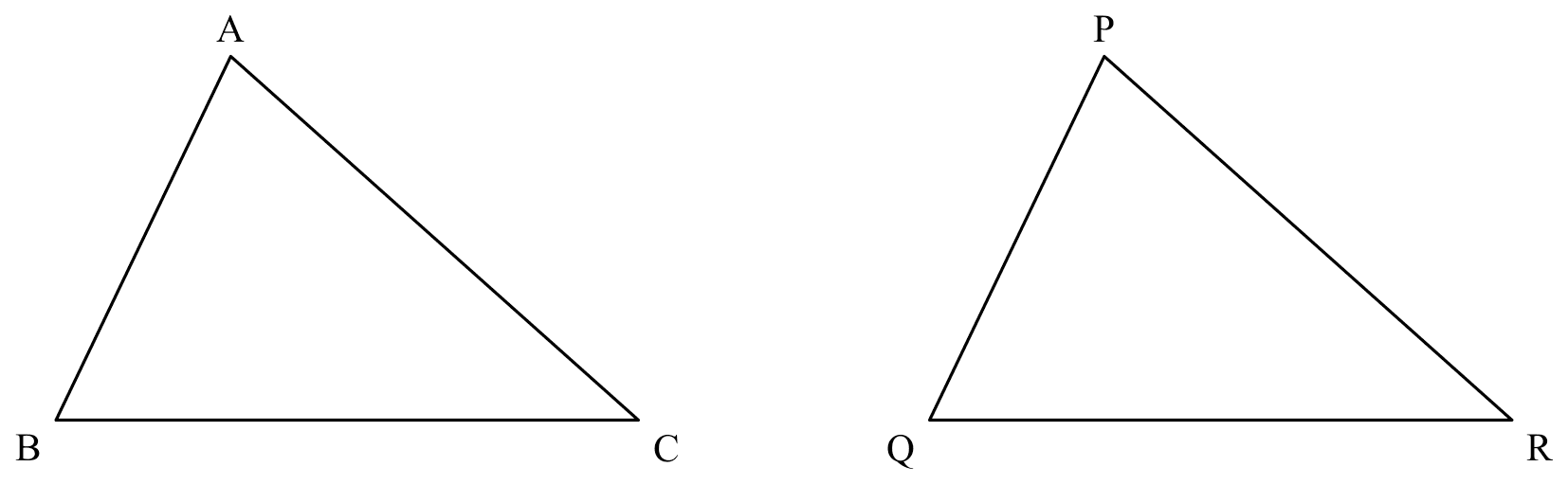
If
If $\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$,
Then
$\angle ABC=\angle PQR$
$\angle BCA=\angle QRP$
$\angle ACB=\angle PRQ$
corr. sides, $\cong$ $\triangle$s
corr. sides, $\cong$ $\triangle$s
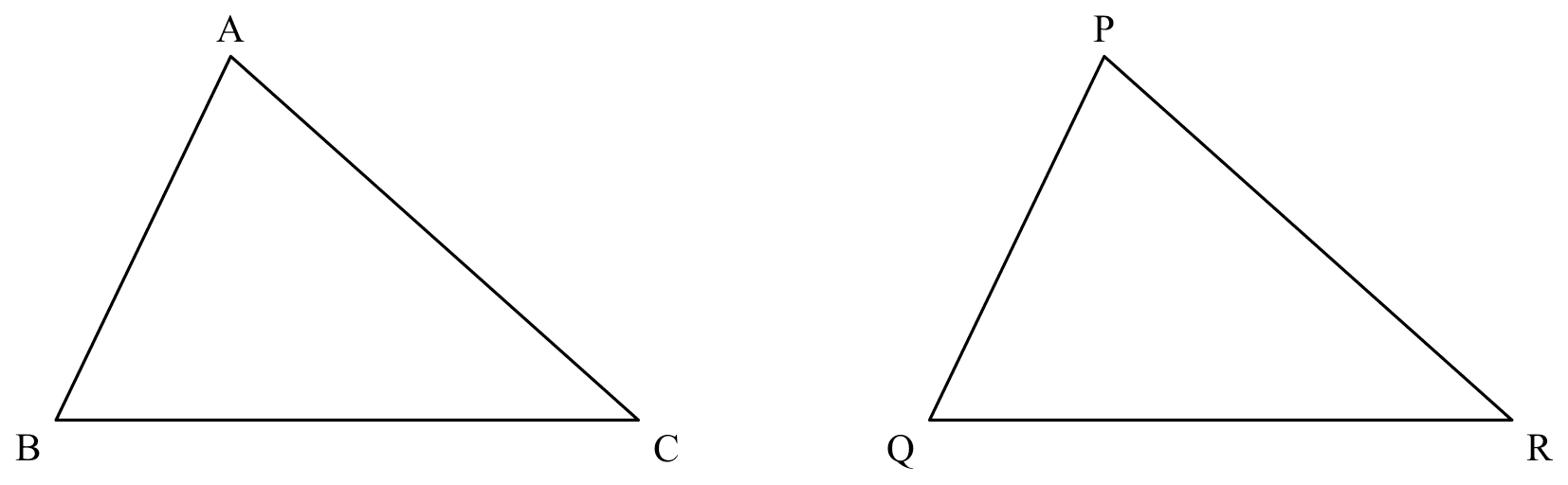
If
If $\triangle ABC \cong \triangle PQR$,
Then
$AB=PQ$
$BC=QR$
$AC=PR$
corr. $\angle$s, $\sim$ $\triangle$s
corr. $\angle$s, $\sim$ $\triangle$s
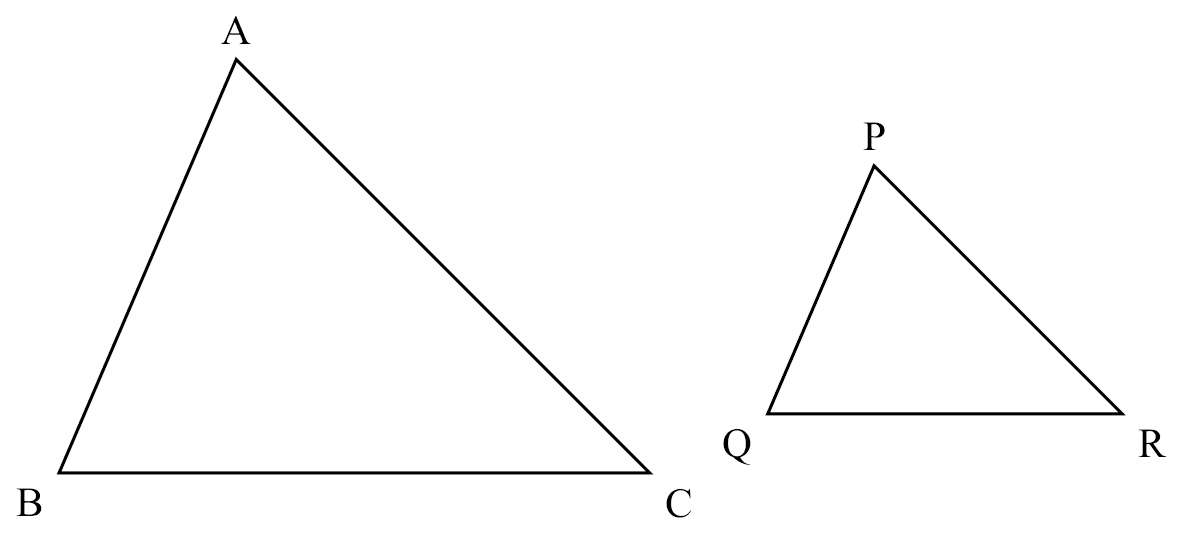
If
If $\triangle ABC \sim \triangle PQR$,
Then
$\angle ABC=\angle PQR$
$\angle BCA=\angle QRP$
$\angle ACB=\angle PRQ$
corr. sides, $\sim$ $\triangle$s
corr. sides, $\sim$ $\triangle$s
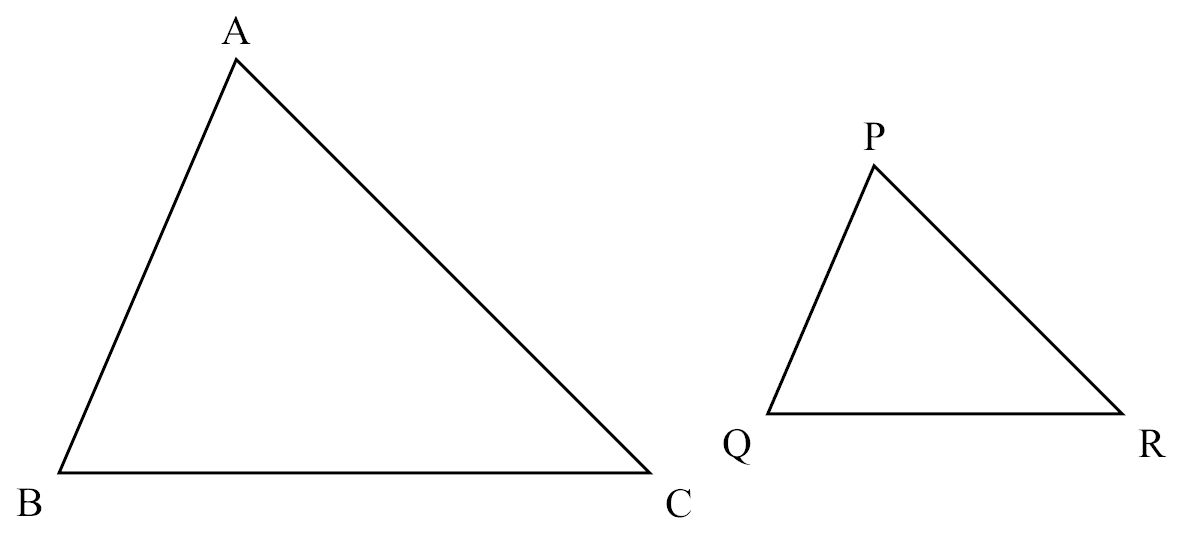
If
If $\triangle ABC \sim \triangle PQR$,
Then
$\frac{AB}{PQ}=\frac{BC}{QR}=\frac{AC}{PR}$
base $\angle$s, isos. $\triangle$
base $\angle$s, isos. $\triangle$
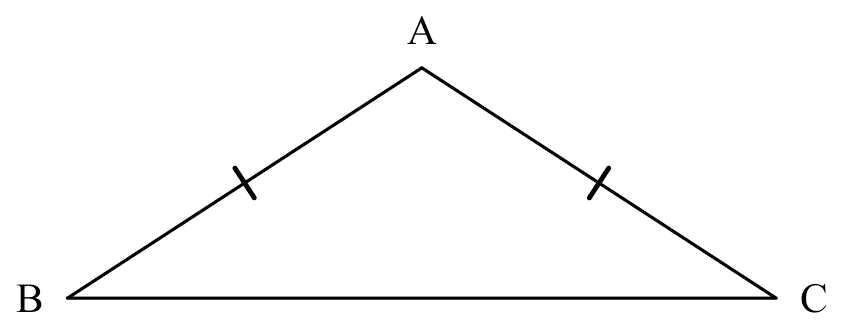
If
If $AB = BC$,
Then
$\angle ABC = \angle ACB$
sides opp. equal $\angle$s
sides opp. equal $\angle$s
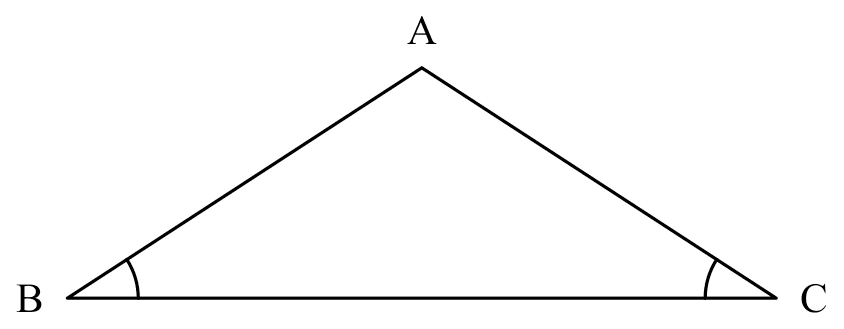
If
If $\angle ABC = \angle ACB$,
Then
$AB = AC$
property of isos. $\triangle$
property of isos. $\triangle$
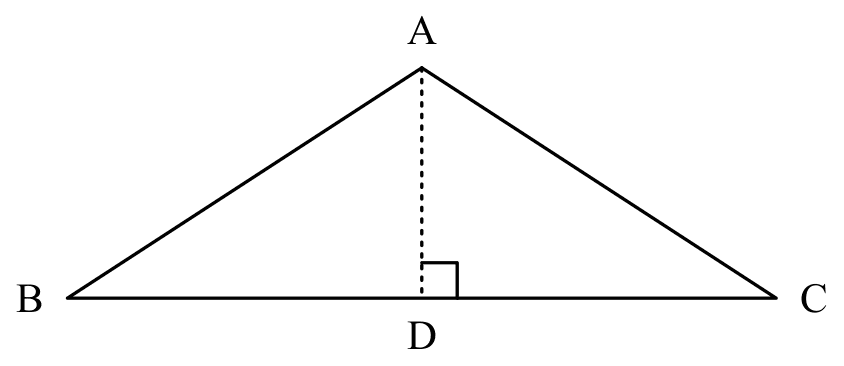
If
If $\triangle ABC$ is isosceles ($AB = AC$),
Then
$\angle BAD=\angle CAD$
$BD=CD$
$AD \perp BC$
property of equil. $\triangle$
property of equil. $\triangle$
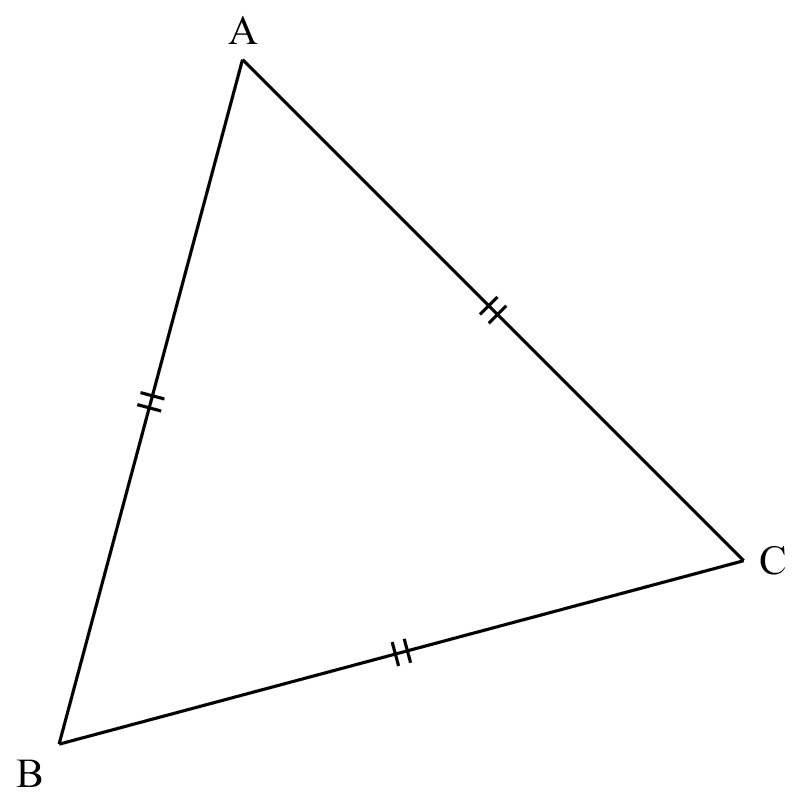
If
If $\triangle ABC$ is equilateral ($AB=BC=AC$),
Then
$\angle ABC = \angle ACB = \angle BAC = 60^{\circ}$
pyth. thm
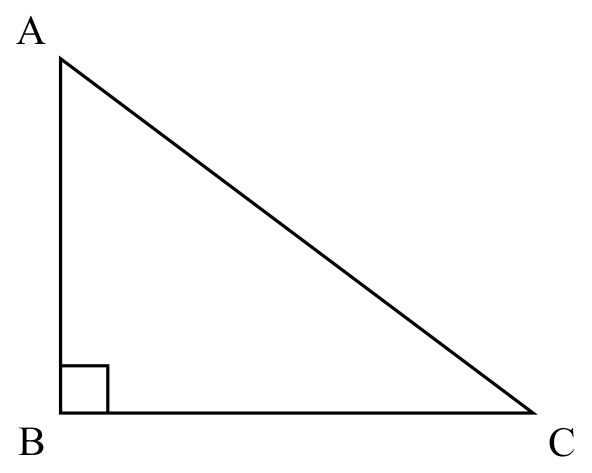
If
If $\triangle ABC$ is right-angled (at B),
Then
$AB^{2} + BC^{2} = AC^{2}$
converse of pyth. thm
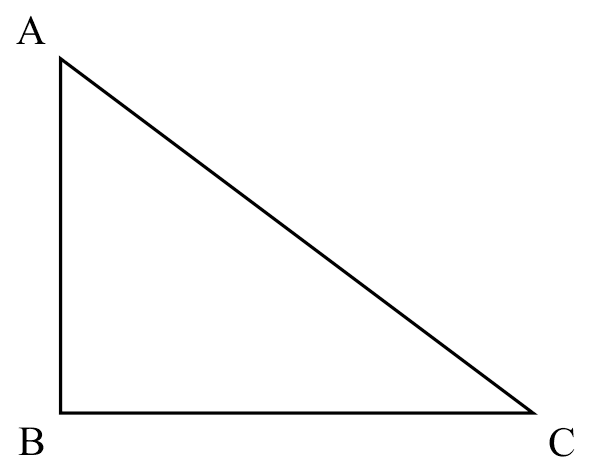
If
If $AB^{2} + BC^{2} = AC^{2}$,
Then
$\triangle ABC$ is right-angled and $\angle ABC = 90^{\circ}$
triangle inequality
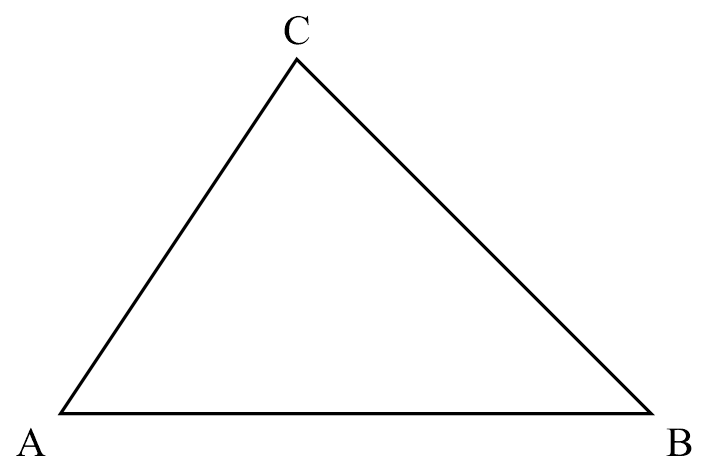
$AB+AC>BC$
$AB+BC>AC$
$AC+BC>AB$
Quadrilaterals
$\angle$ sum of polygon
$\angle$ sum of polygon
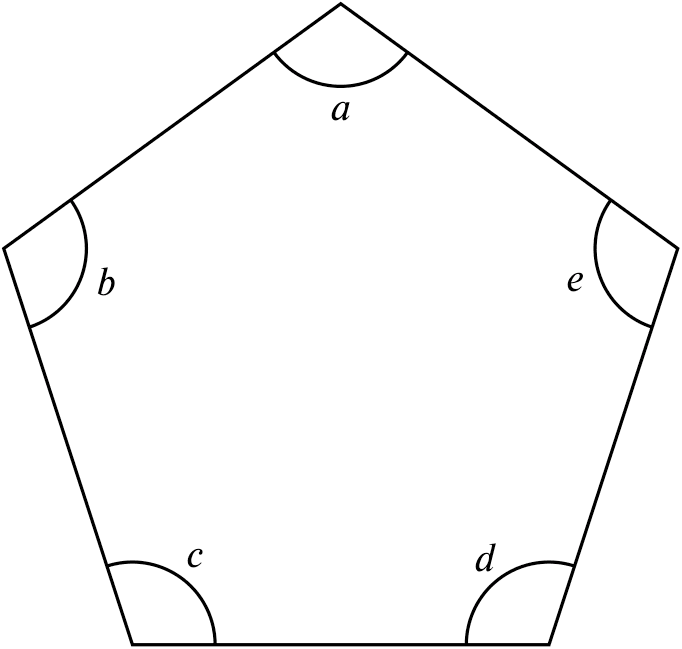
$\text{Sum of interior angles}= (n-2)\times180^{\circ}$
e.g. sum of interior angles of pentagon $(5-2)\times180^{\circ}=540^{\circ}$
$a+b+c+d+e=540^{\circ}$
sum of ext. $\angle$s of polygon
sum of ext. $\angle$s of polygon
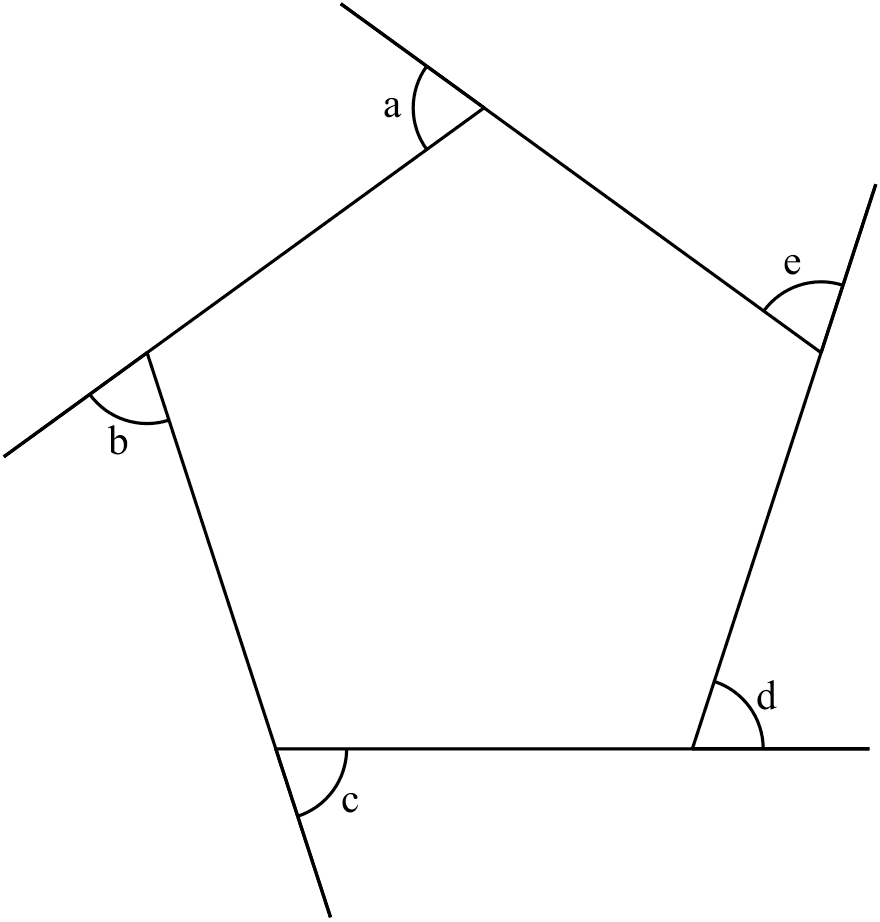
$\text{Sum of exterior angles}= 360^{\circ}$
e.g. $a+b+c+d+e=360^{\circ}$
opp. sides of $\parallel$gram
opp. sides of $\parallel$gram

If
If $ABCD$ is a parallelogram,
Then
$AB = DC$
$AD = BC$
opp. $\angle$s of $\parallel$gram
opp. $\angle$s of $\parallel$gram

If
If $ABCD$ is a parallelogram,
Then
$\angle DAB = \angle BCD$
$\angle ADB = \angle ABC$
diags. of $\parallel$gram
diags. of $\parallel$gram
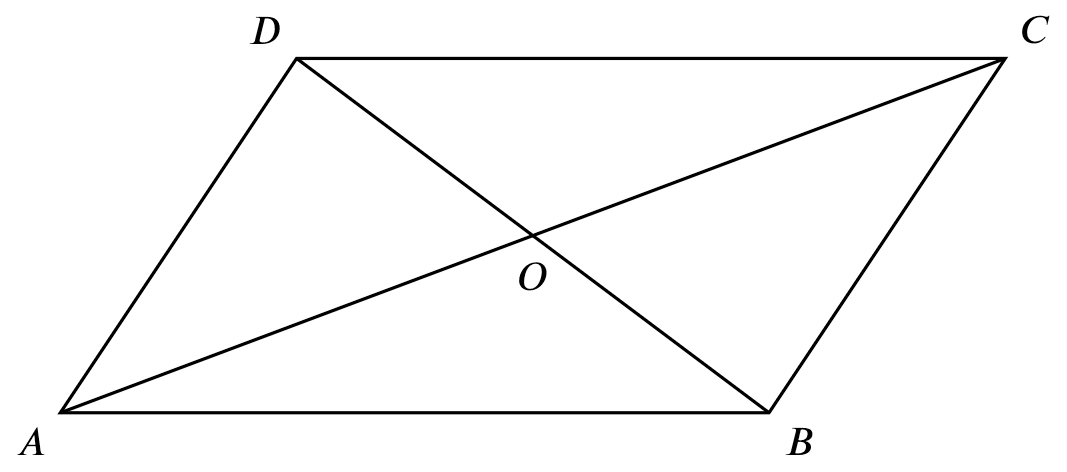
If
If $ABCD$ is a parallelogram,
Then
$OD=OB$
$OA=OC$
diagonals bisect area of $\parallel$gram
diagonals bisect area of $\parallel$gram
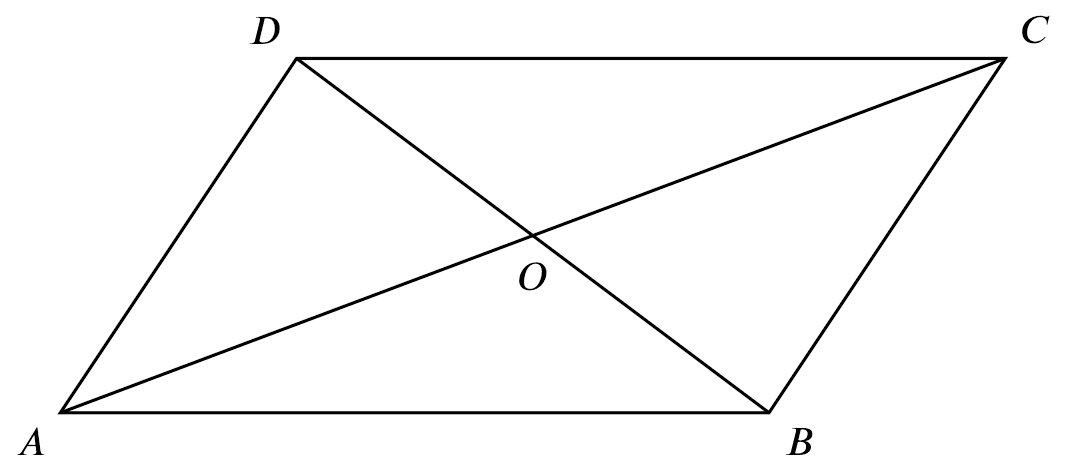
If
If $ABCD$ is a parallelogram,
Then
$\text{Area of }\triangle ACD = \text{Area of }\triangle ACB$
$\text{Area of }\triangle ABD = \text{Area of }\triangle CBD$
opp. sides equal
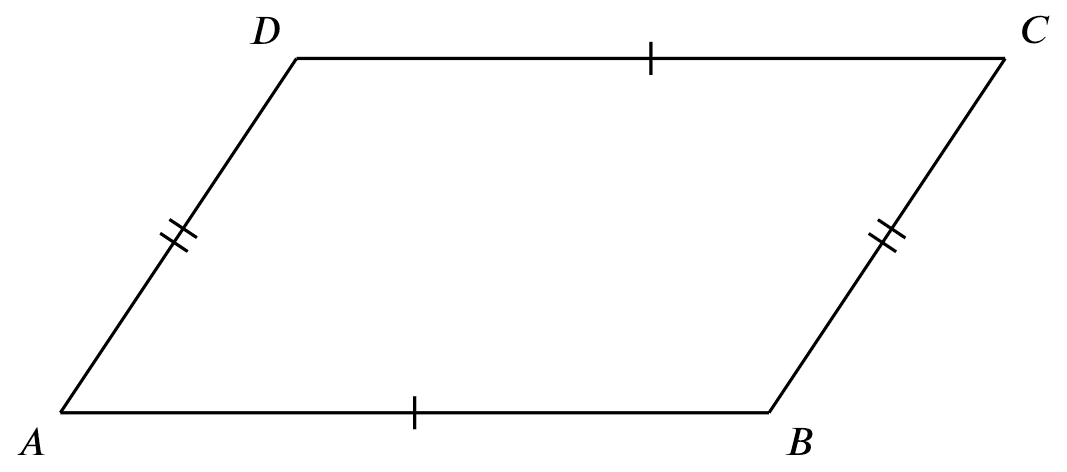
If
If $AB = DC$ and $AD = BC$,
Then
$ABCD$ is a parallelogram
opp. $\angle$s equal
opp. $\angle$s equal
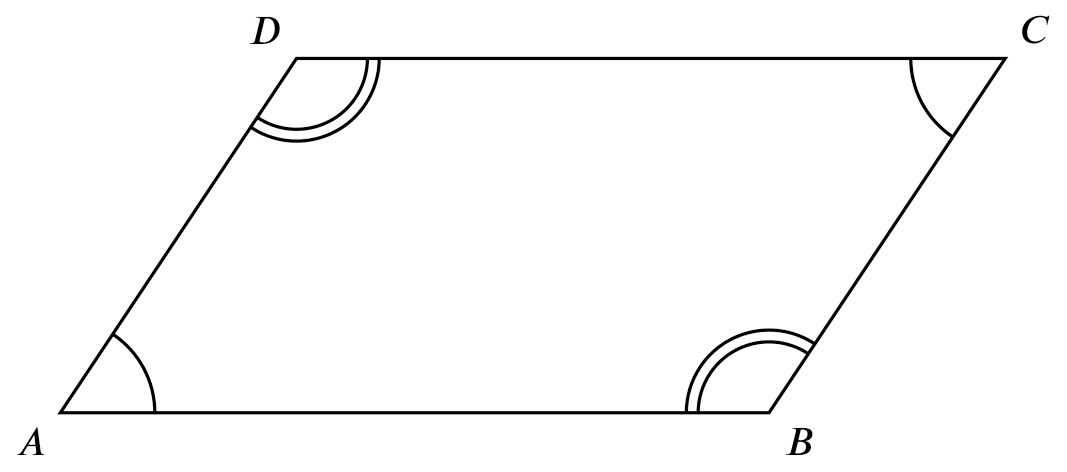
If
If $\angle ADC=\angle ABC$ and $\angle DAB=\angle DCB$,
Then
$ABCD$ is a parallelogram
diags. bisect each other
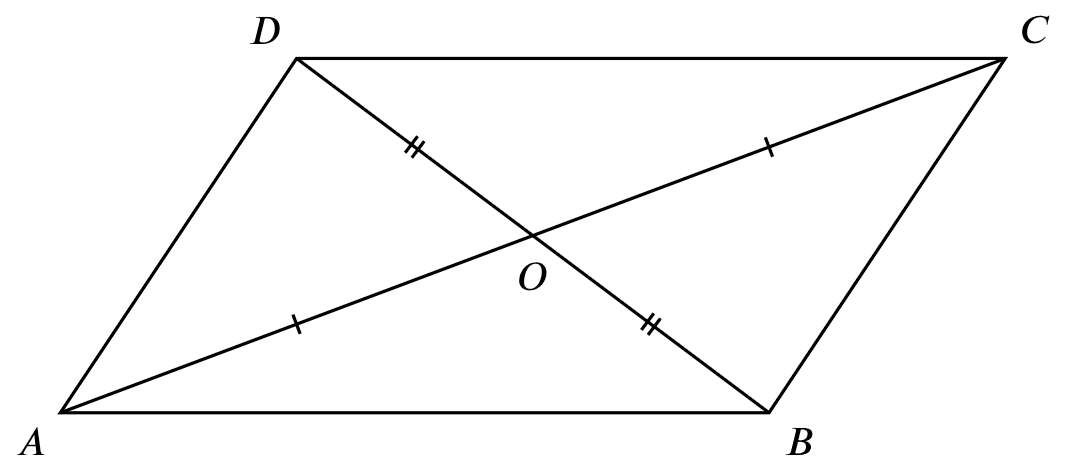
If
If $OA = OC$ and $OD = OB$,
Then
$ABCD$ is a parallelogram
opp. sides equal and $\parallel$
opp. sides equal and $\parallel$
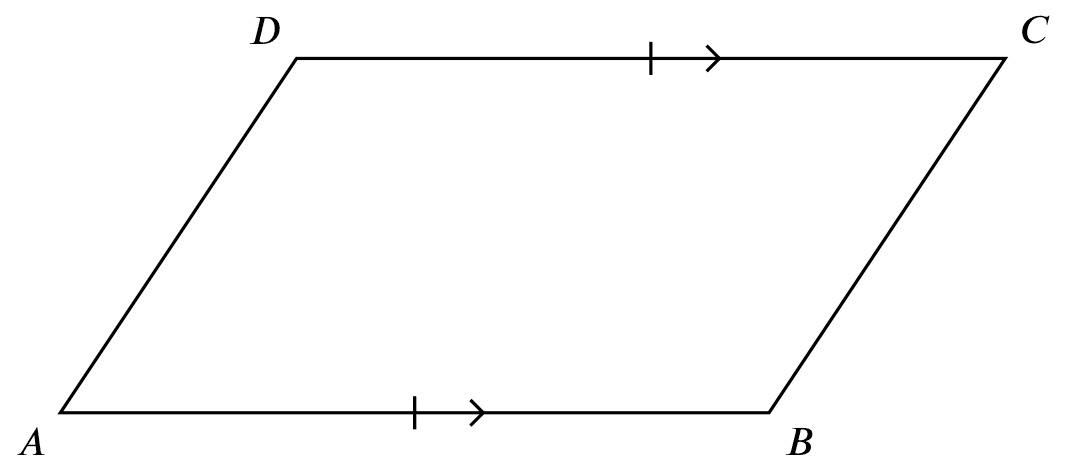
If
If $AB = DC$ and $DC \parallel AB$,
Then
$ABCD$ is a parallelogram
property of square
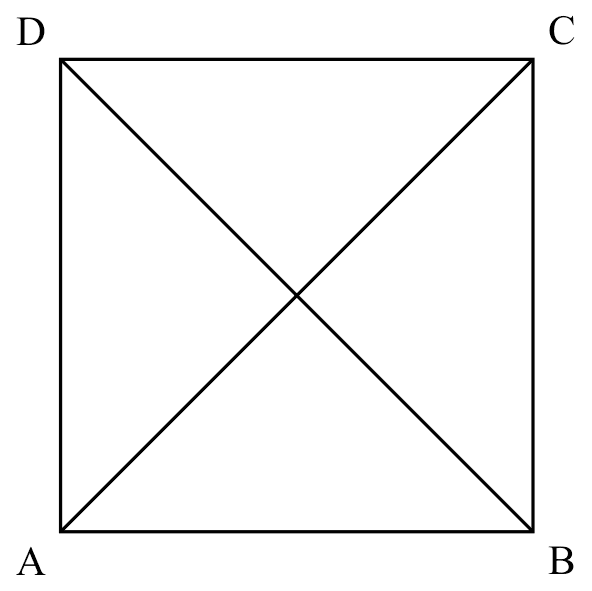
If
If $ABCD$ is a square,
Thenit posses all properties of a parallelogram
$AC=BD$
$AC \perp BD$
$\angle ADC= \angle DCB = \angle CBA = \angle BAD =90^{\circ}$
$AB=BC=CD=DA$
$DB$ bisects $\angle ABC$ and $\angle ADC$
$AC$ bisects $\angle DAB$ and $\angle DCB$
property of rectangle
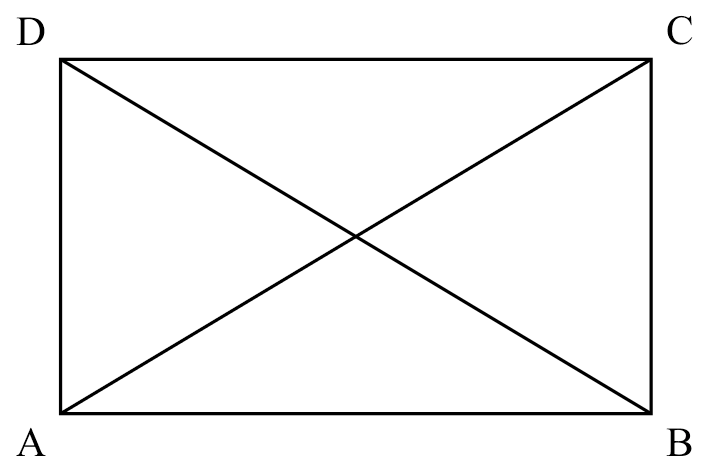
If
If $ABCD$ is a rectangle,
Thenit posses all properties of a parallelogram
$AC=BD$
$\angle ADC= \angle DCB = \angle CBA = \angle BAD =90^{\circ}$
property of rhombus
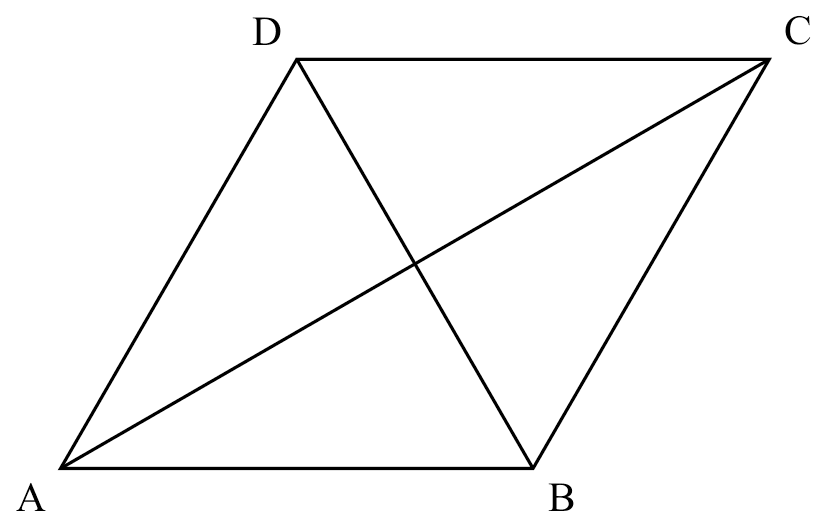
If
If $ABCD$ is a rhombus,
Thenit posses all properties of a parallelogram
$AB=BC=CD=DA$
$AC \perp BD$
$AC$ bisects $\angle BAD$ and $\angle BCD$
$BD$ bisects $\angle ABC$ and $\angle ADC$
property of kite
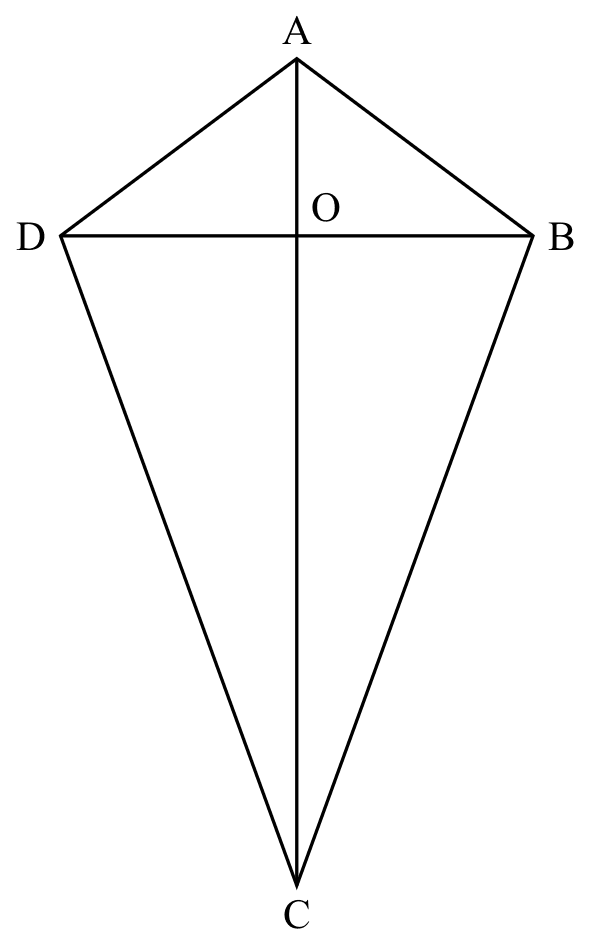
If
If $ABCD$ is a kite,
Then
$AC \perp BD$
$AD=DB$
$DC=BC$
$OD=OB$
$\angle DAO=\angle BAO$
$\angle DCO =\angle BCO$
property of trapezium
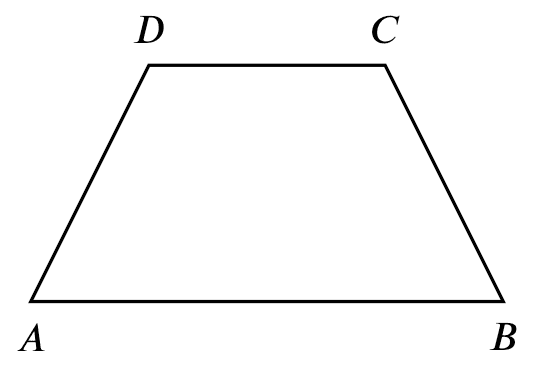
If
If $ABCD$ is a trapezium,
Then
$DC \parallel AB$
$\angle CDA + \angle DAB = 180^{\circ}$
$\angle DCB + \angle CBA = 180^{\circ}$
Circles
Let O be the centre of all the circles below.
line from centre $\perp$ chord bisects chord
line from centre $\perp$ chord bisects chord
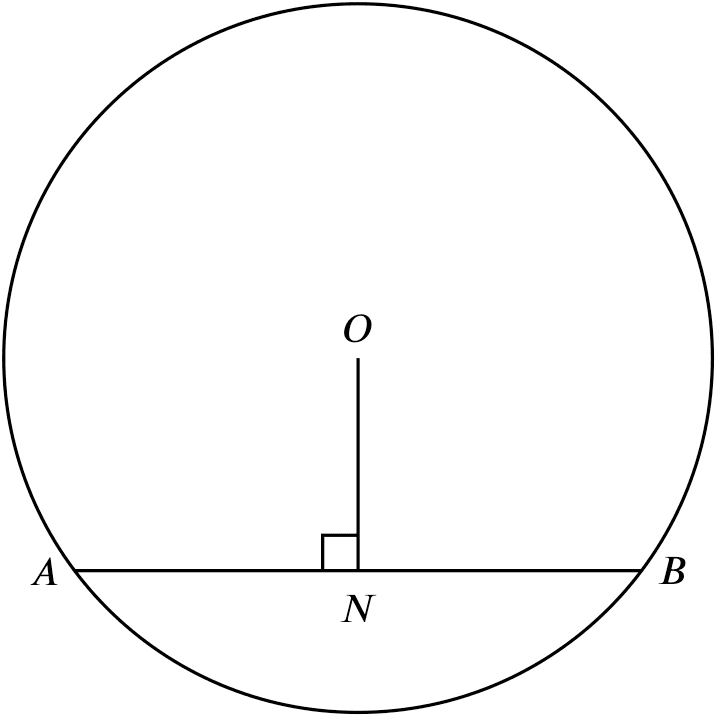
If
If $ON \perp AB$,
Then
$AN = NB$
line joining centre to mid-pt. of chord $\perp$ chord
line joining centre to mid-pt. of chord $\perp$ chord
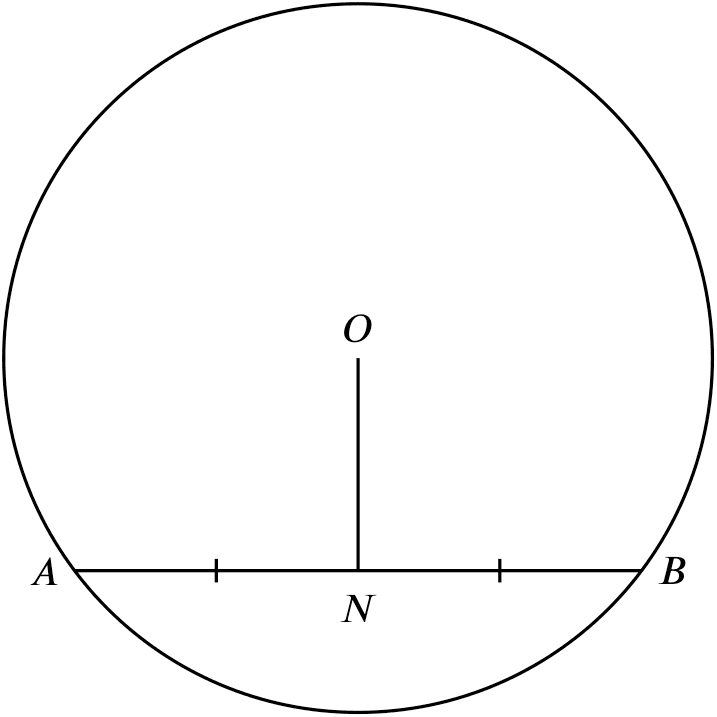
If
If $AN = NB$,
Then
$ON \perp AB$ ($\angle ANO$ and $\angle ONB = 90^{\circ}$)
$\perp$ bisector of chord passes through center
$\perp$ bisector of chord passes through center
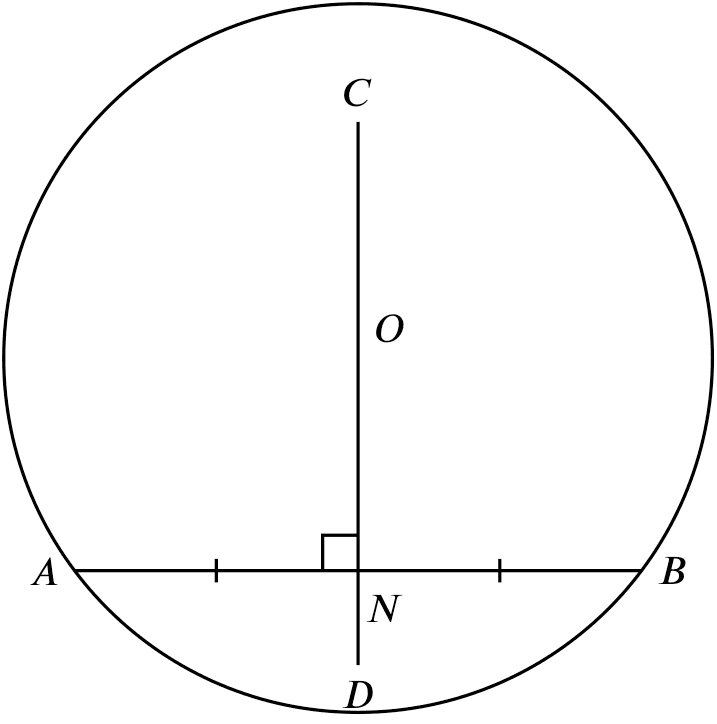
If
If $AN = NB$ and $CD \perp AB$,
Then
$CD$ passes through the center O
equal chords, equidistant from centre
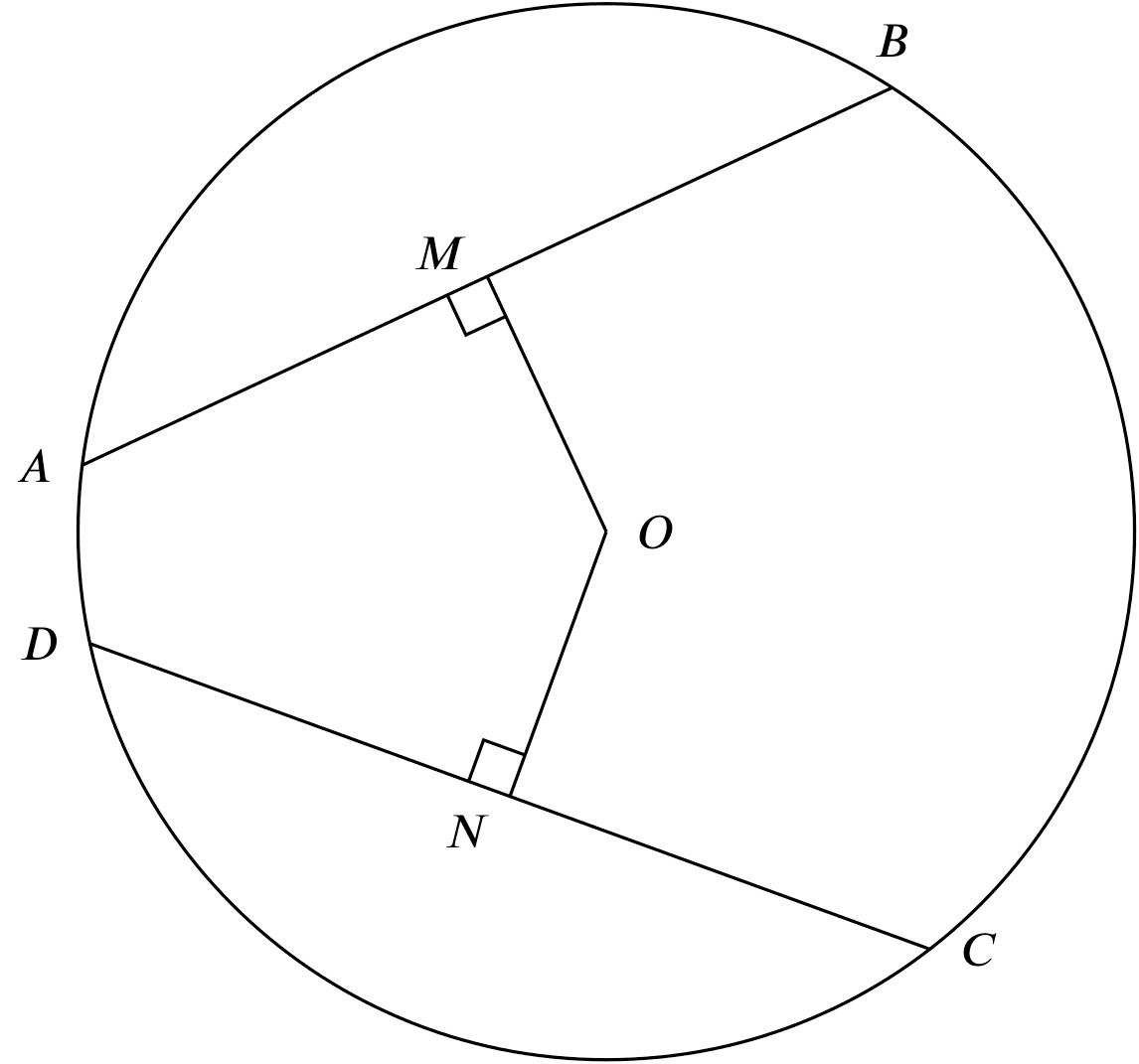
If
If $AB = CD$ and $OM \perp AB$ and $ON \perp CD$,
Then
$OM = ON$
chords equidistant from centre are equal
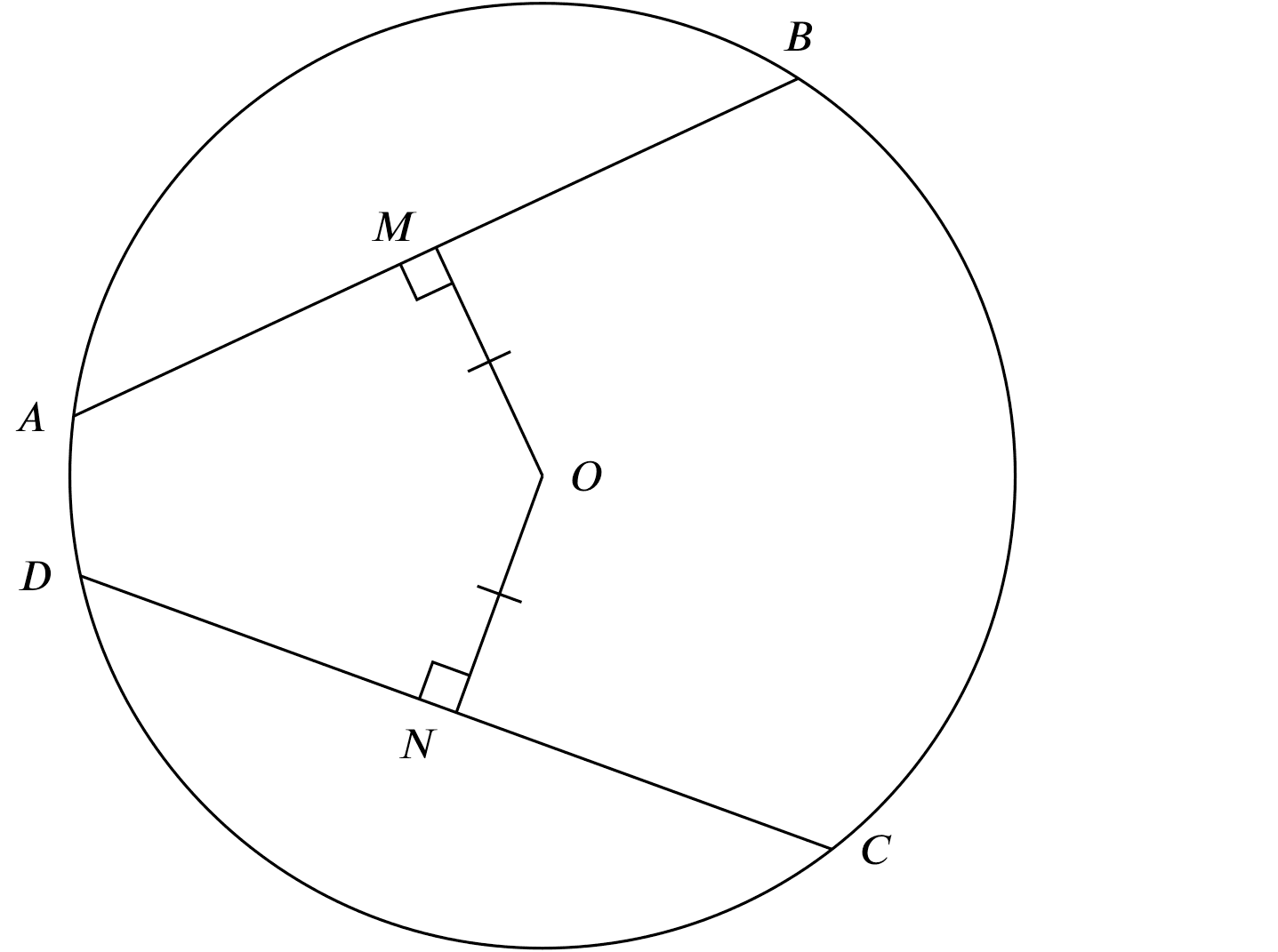
If
If $OM = ON$ and $OM \perp AB$ and $ON \perp CD$,
Then
$AB = CD$
$\angle$ at center twice $\angle$ at ☉$^{ce}$
$\angle$ at center twice $\angle$ at ☉$^{ce}$
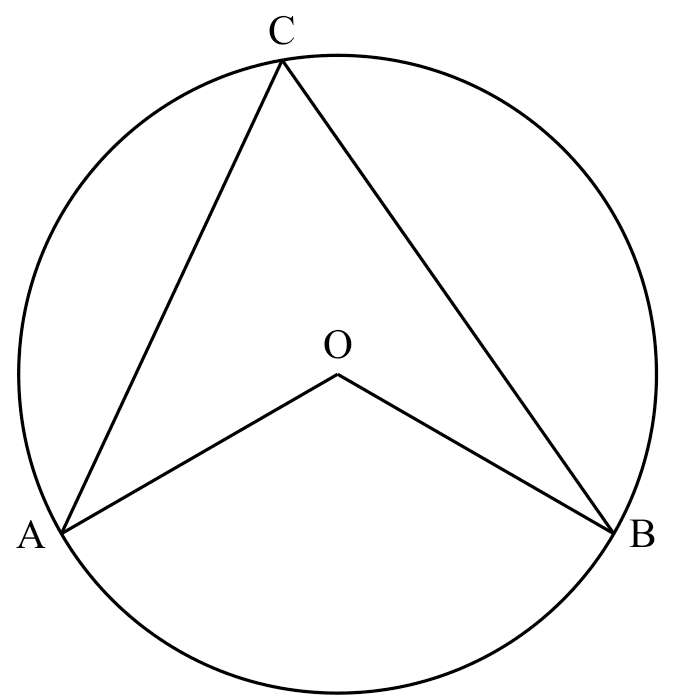
$\angle AOB = 2\,\angle ACB$
$\angle$ in semi-circle
$\angle$ in semi-circle
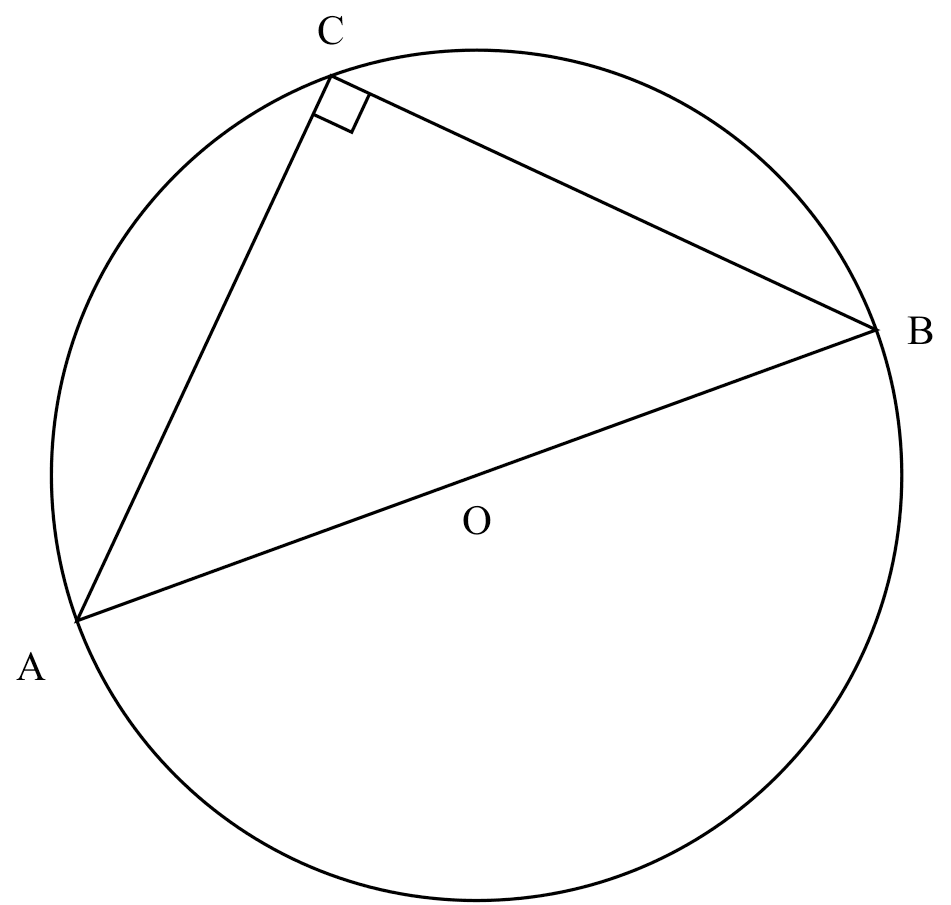
If
If AB is the diameter of the circle,
Then
$\angle ACB = 90^{\circ}$
$\angle$s in the same segment
$\angle$s in the same segment
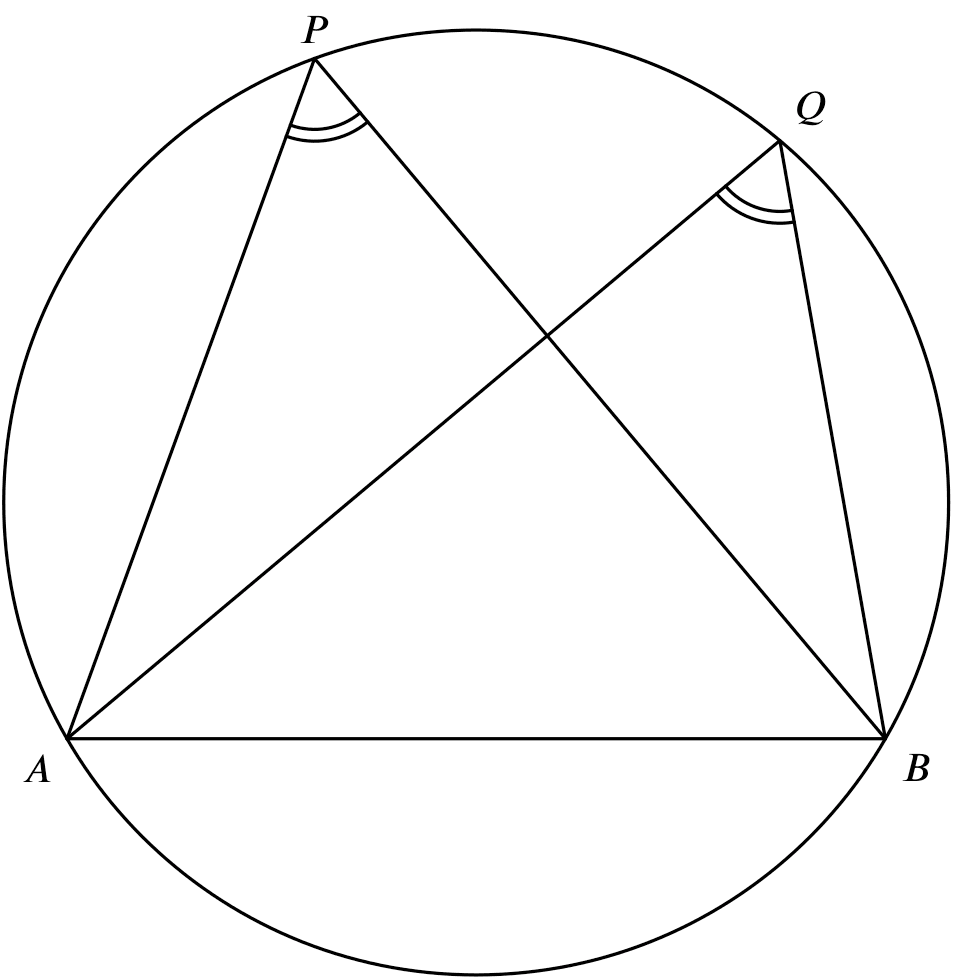
$\angle APB = \angle AQB$
arcs proportional to $\angle$s at centre
arcs proportional to $\angle$s at centre
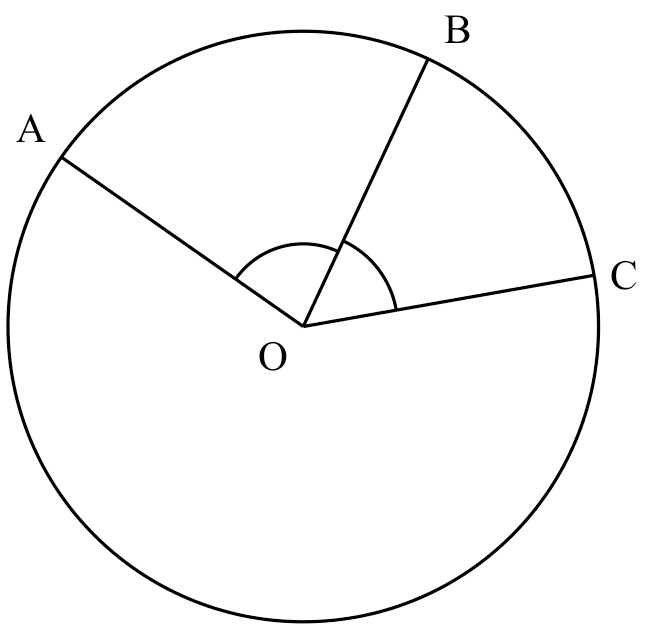
$\overset{\frown}{AB}: \overset{\frown}{BC}= \angle AOB : \angle BOC$
arcs proportional to $\angle$s at circumference
arcs proportional to $\angle$s at circumference
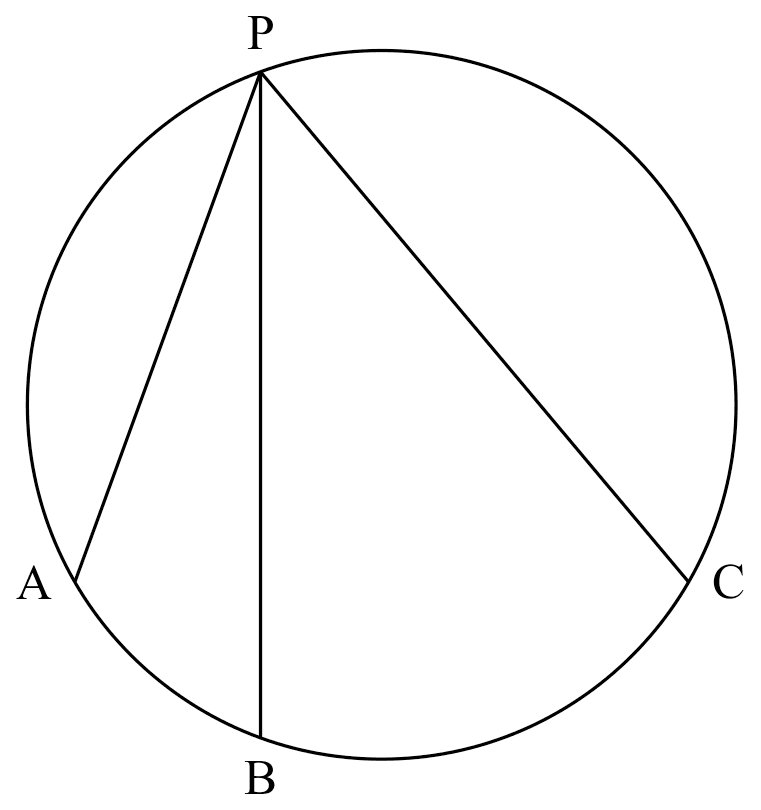
$\overset{\frown}{AB}: \overset{\frown}{BC}= \angle APB : \angle BPC$
equal chords, equal arcs
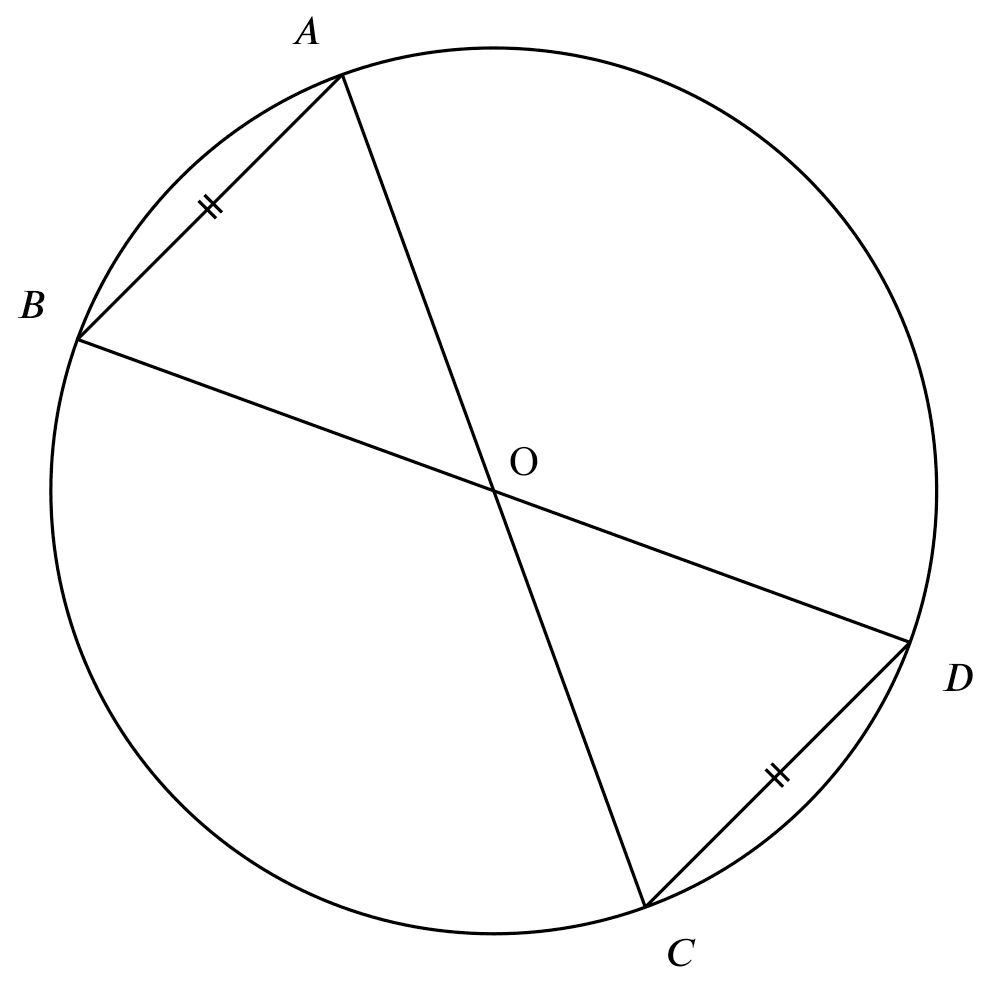
If
If $AB = CD$,
Then
$\overset{\frown}{AB}= \overset{\frown}{CD}$
equal arcs, equal chords
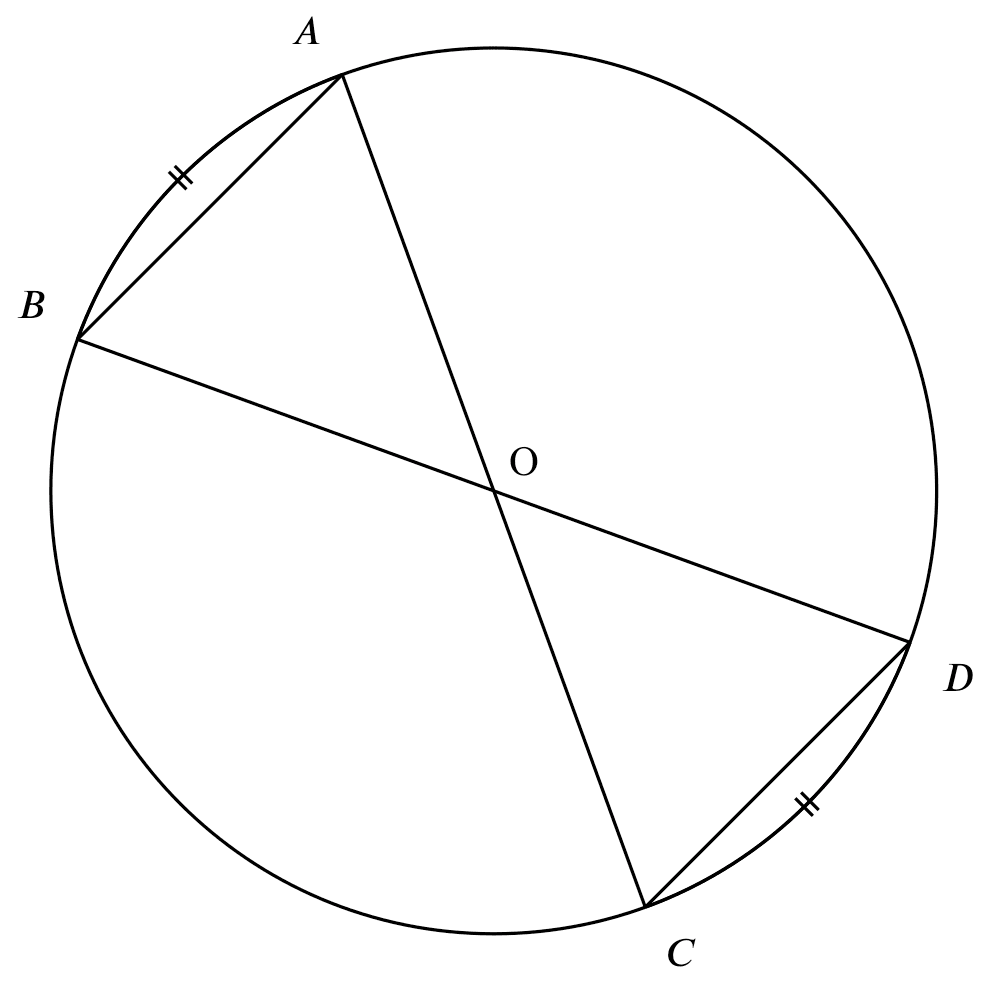
If
If $\overset{\frown}{AB}= \overset{\frown}{CD}$,
Then
$AB = CD$
equal arcs, equal $\angle$s
equal arcs, equal $\angle$s
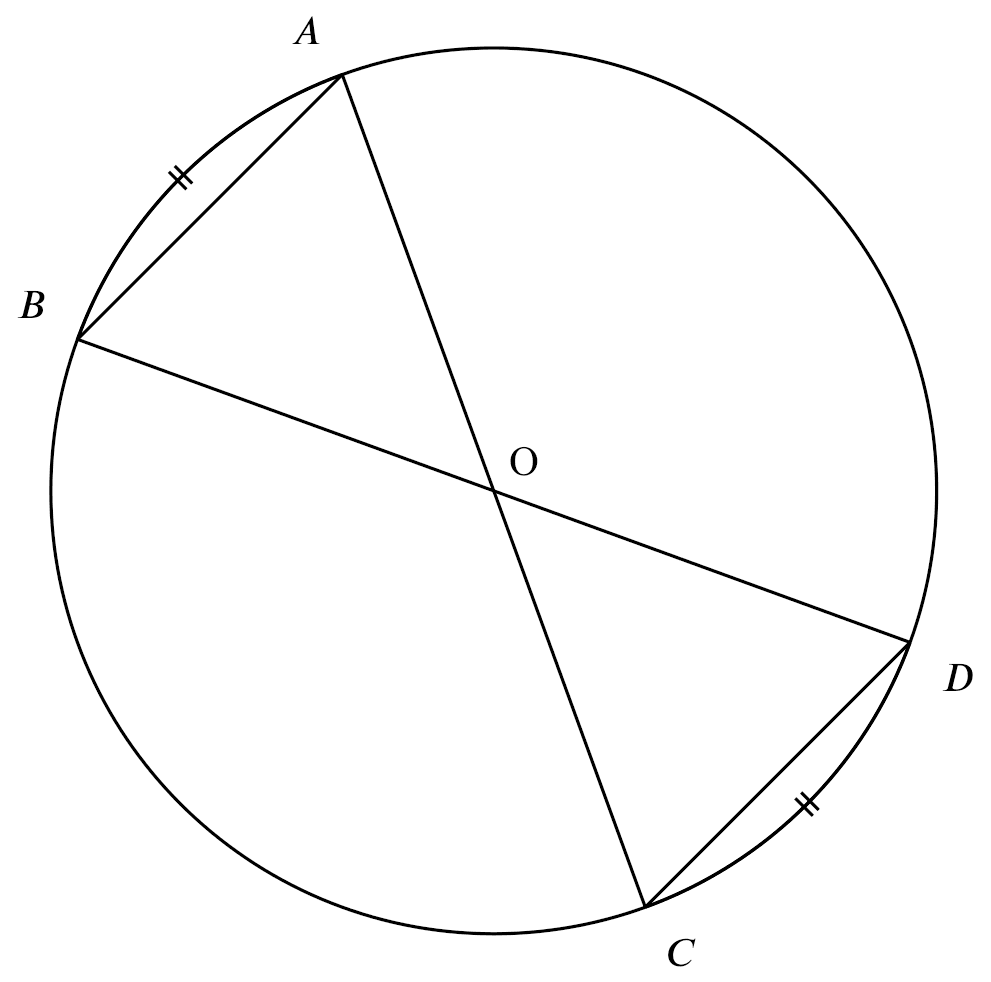
If
If $\overset{\frown}{AB}= \overset{\frown}{CD}$,
Then
$\angle AOB = \angle COD$
equal $\angle$s, equal arcs
equal $\angle$s, equal arcs
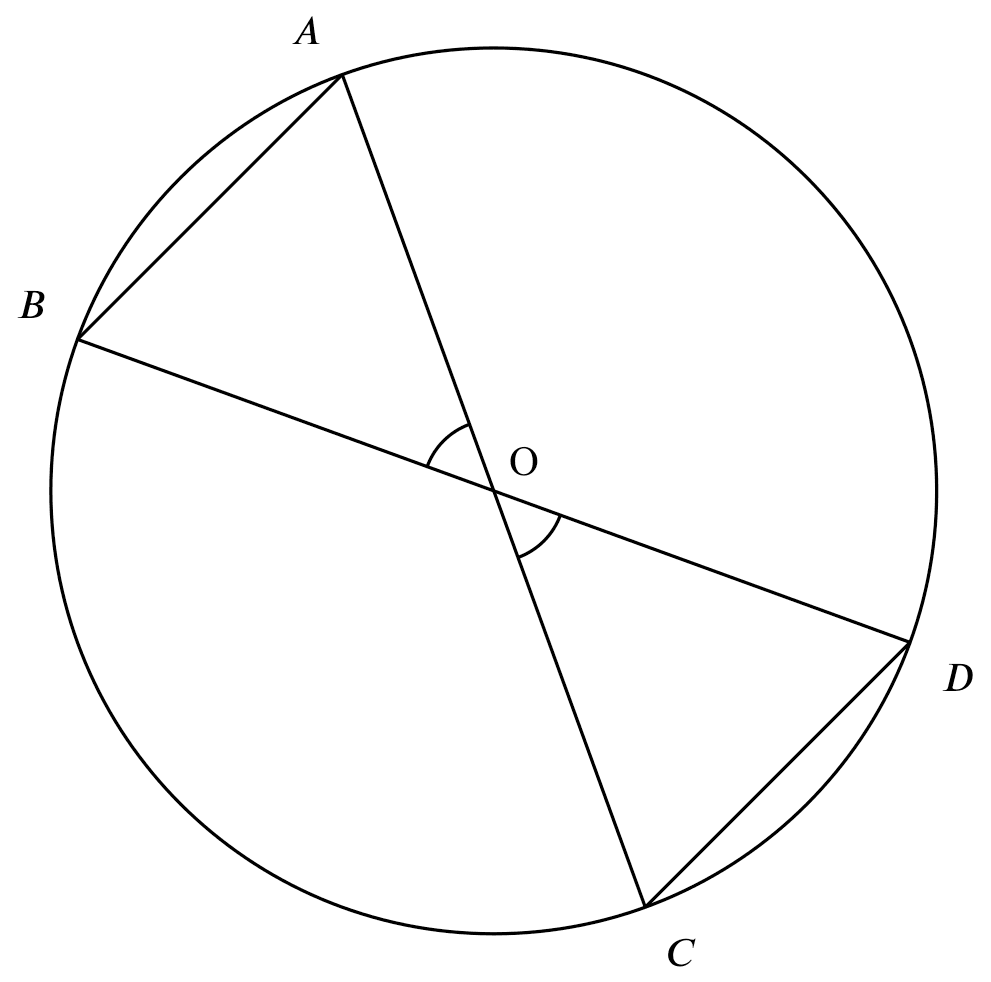
If
If $\angle AOB = \angle COD$,
Then
$\overset{\frown}{AB}= \overset{\frown}{CD}$
equal chords, equal $\angle$s
equal chords, equal $\angle$s
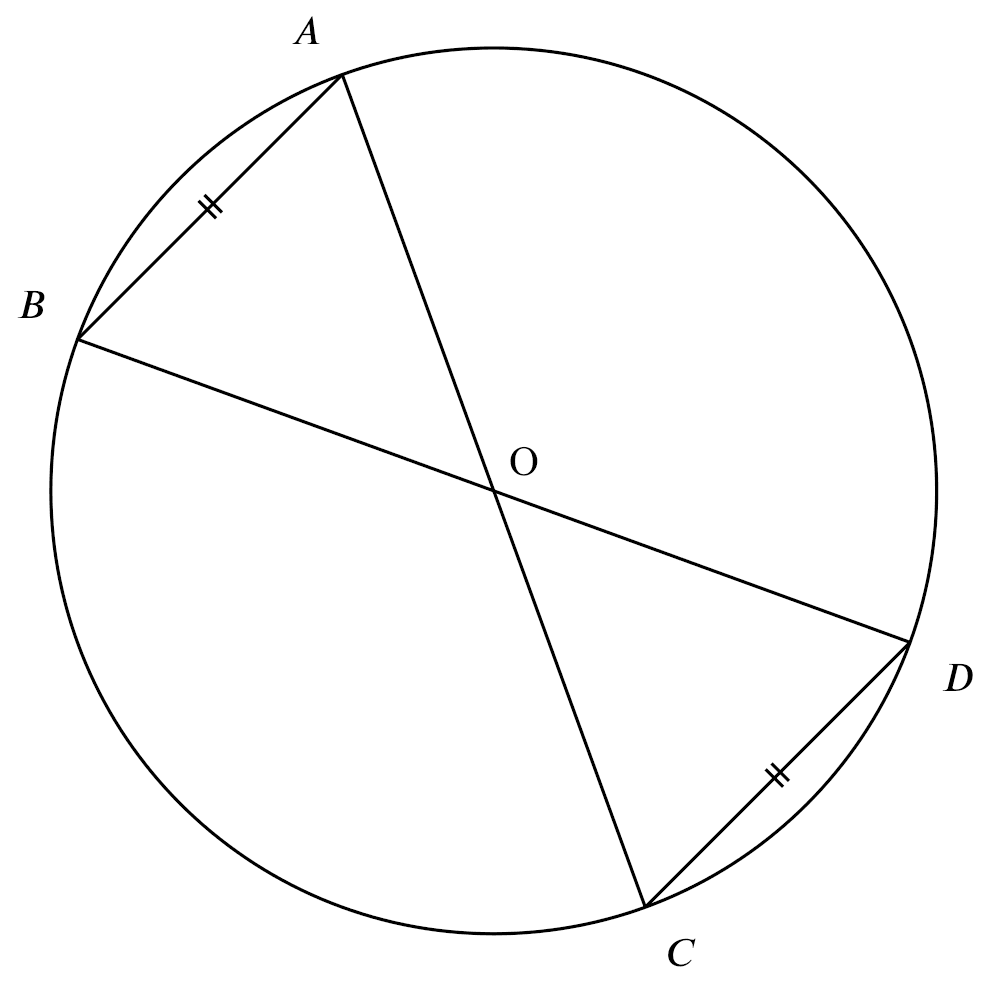
If
If $AB = CD$,
Then
$\angle AOB = \angle COD$
equal $\angle$s, equal chords
equal $\angle$s, equal chords
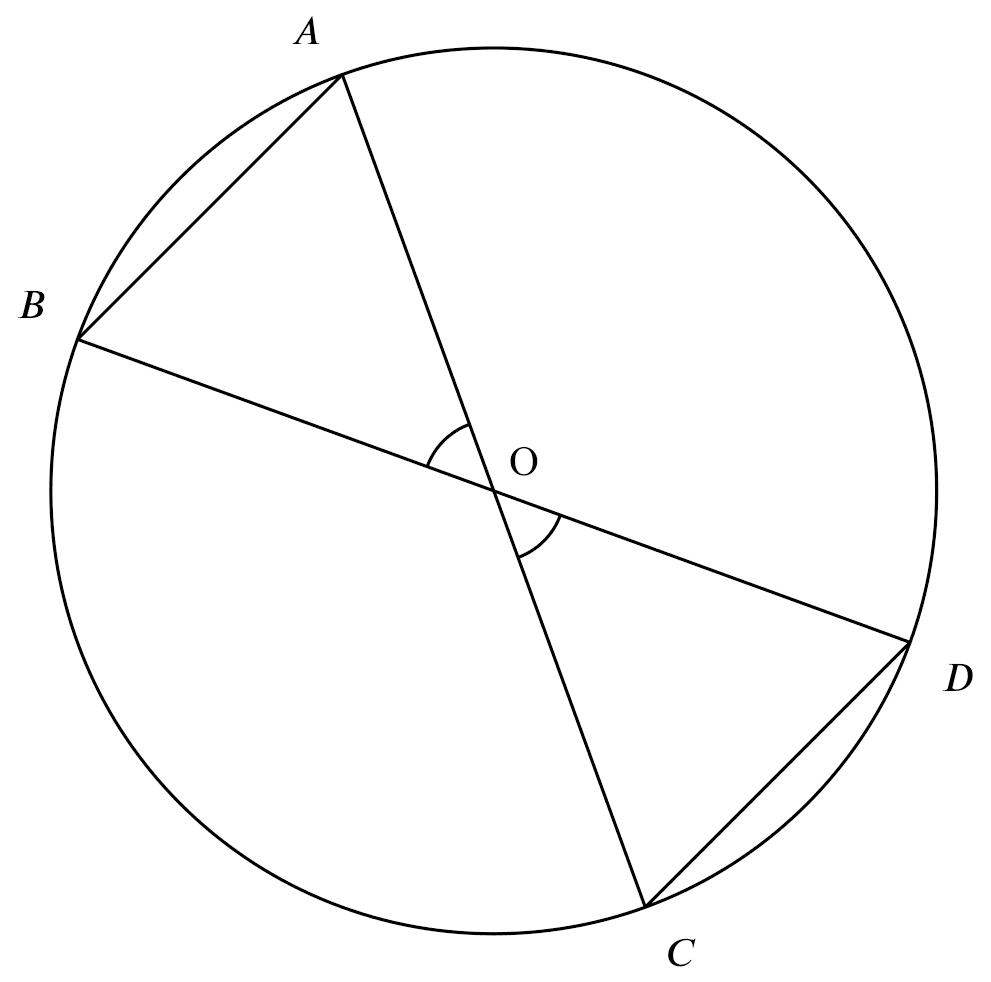
If
If $\angle AOB = \angle COD$,
Then
$AB = CD$
opp. $\angle$s, cyclic quad.
opp. $\angle$s, cyclic quad.
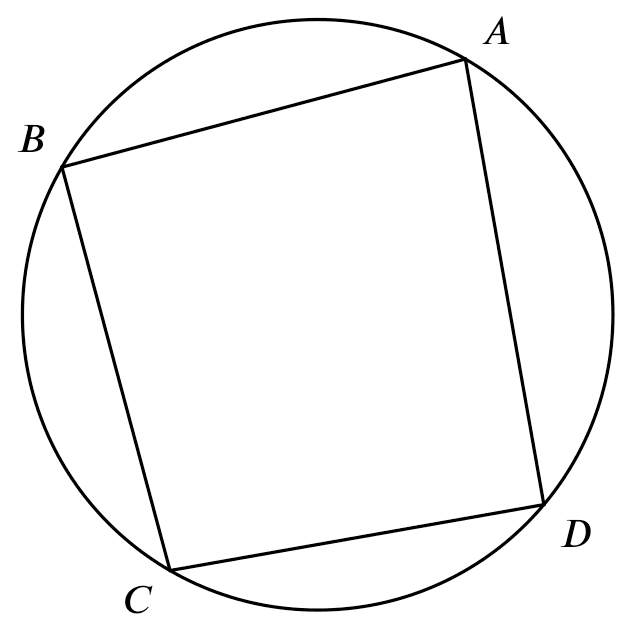
If
If $ABCD$ is a cyclic quadrilateral,
Then
$\angle ABC + \angle ADC = 180^{\circ}$
$\angle BAD + \angle BCD = 180^{\circ}$
ext. $\angle$s, cyclic quad.
ext. $\angle$s, cyclic quad.
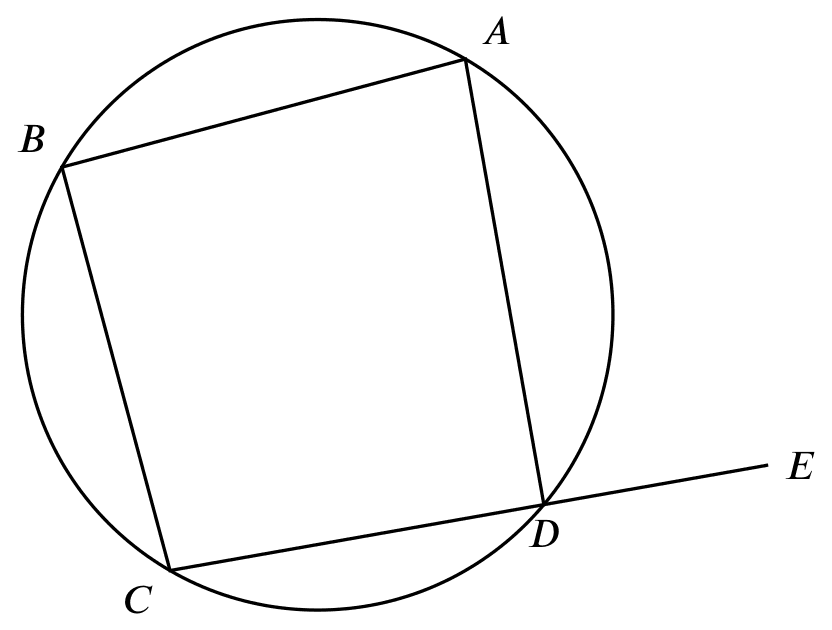
If
If $ABCD$ is a cyclic quadrilateral,
Then
$\angle ABC = \angle ADE$
converse of $\angle$s in the same segment
converse of $\angle$s in the same segment
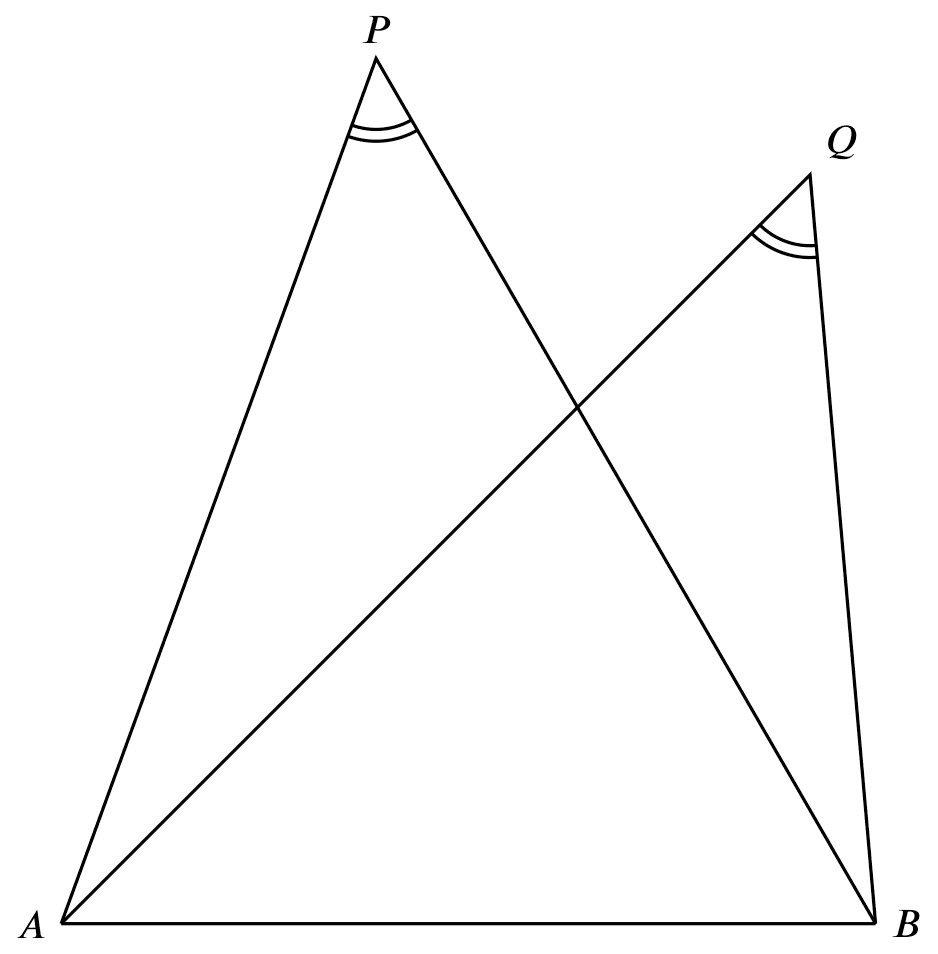
If
If $\angle APB = \angle AQB$,
Then
A,B,Q,P are concyclic
opp. $\angle$s supp.
opp. $\angle$s supp.
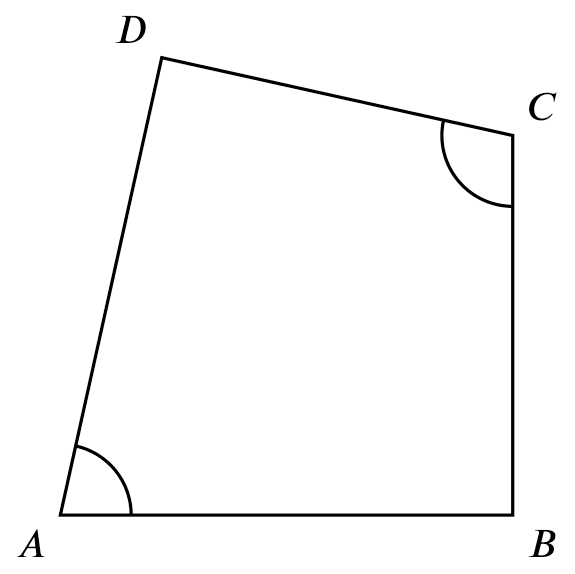
If
If $\angle DAB + \angle BCD = 180^{\circ}$,
Then
$ABCD$ are concyclic
ext. $\angle$ = int. opp. $\angle$
ext. $\angle$ = int. opp. $\angle$
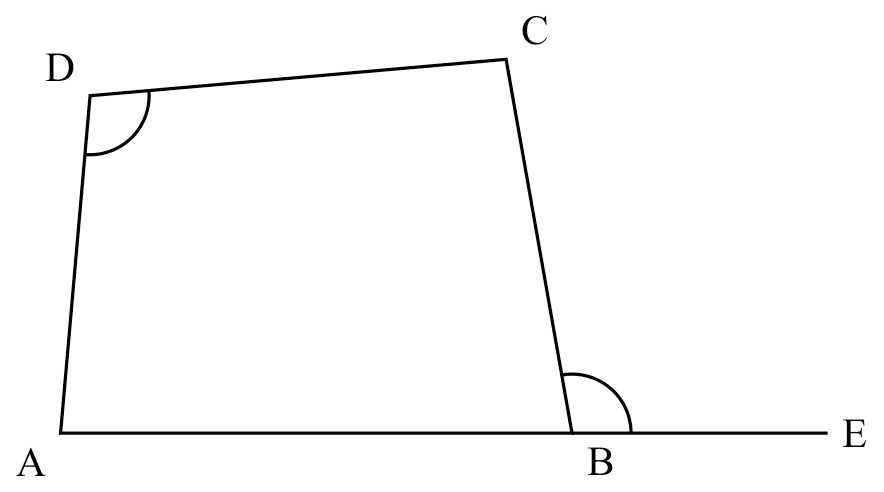
If
If $\angle ADC = \angle CBE$,
Then
$ABCD$ are concyclic
Tangents
tangent $\perp$ radius
tangent $\perp$ radius
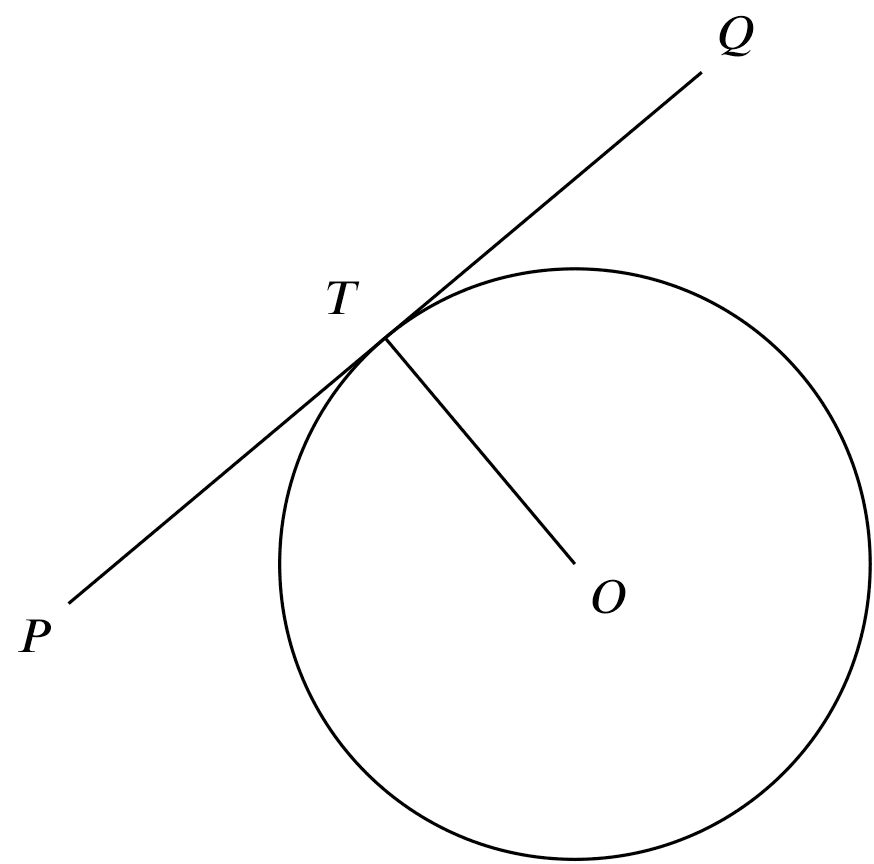
If
If PQ is tangent at T,
Then
$PQ \perp OT$
converse of tangent $\perp$ radius
converse of tangent $\perp$ radius
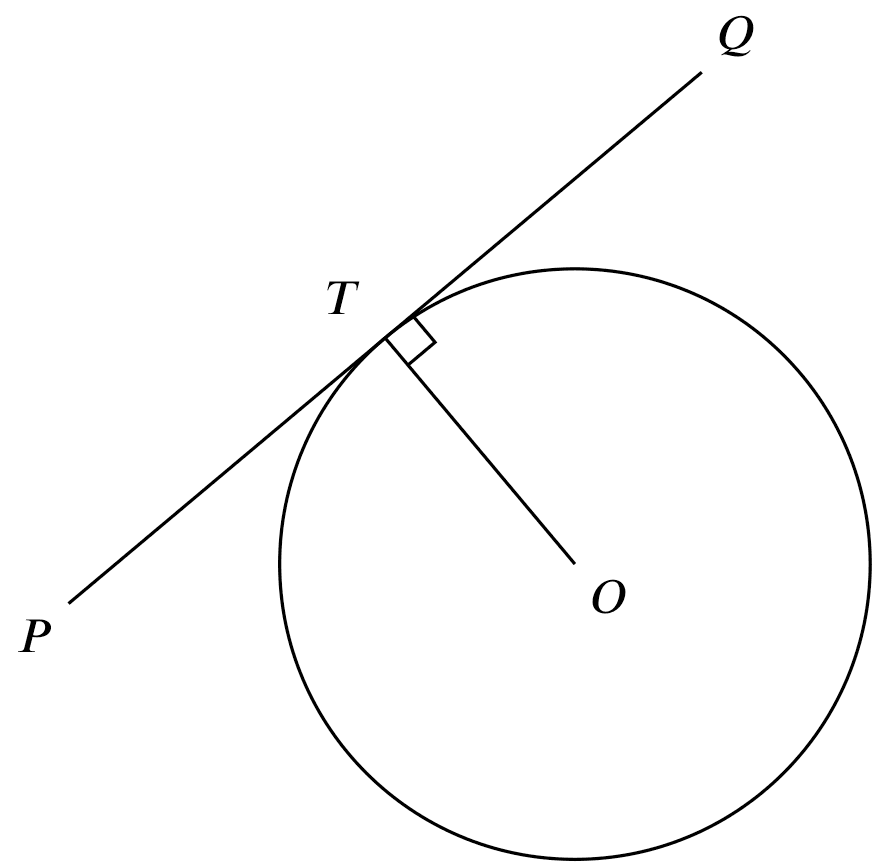
If
If $OT \perp PQ$,
Then
$PQ$ is tangent at T
tangent properties
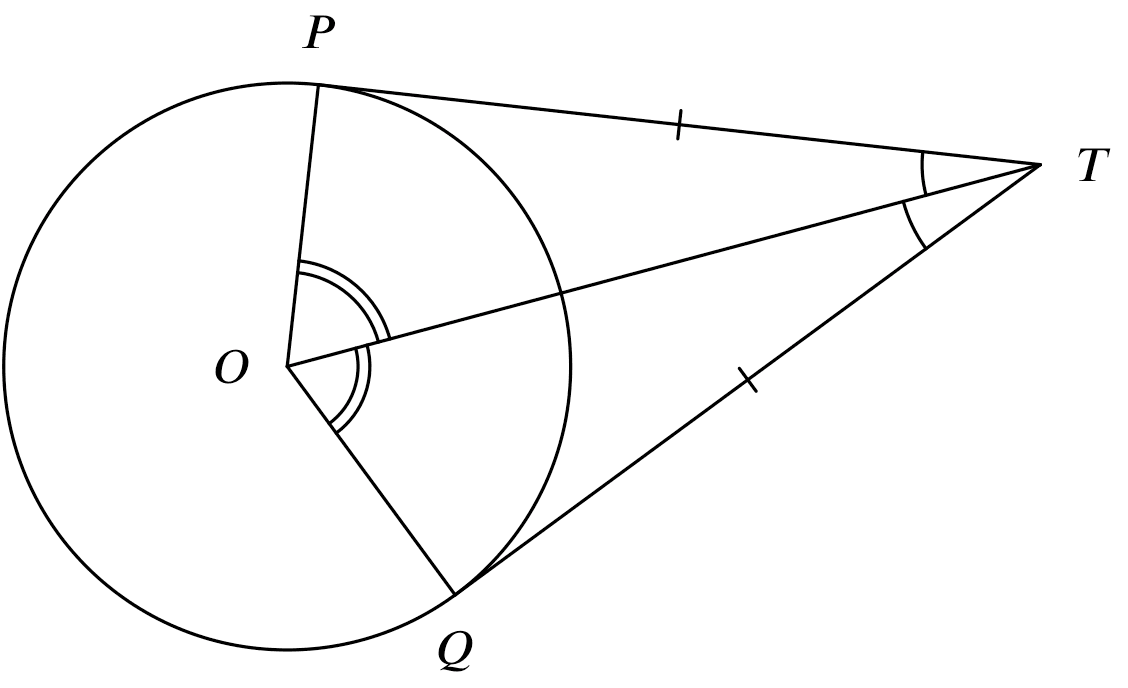
If
If TP and TQ are tangents at P and Q from T,
Then
$\angle TOP=\angle TOQ$
$\angle OTP=\angle OTQ$
$TP= TQ$
$\angle$s in alt. segment
$\angle$s in alt. segment
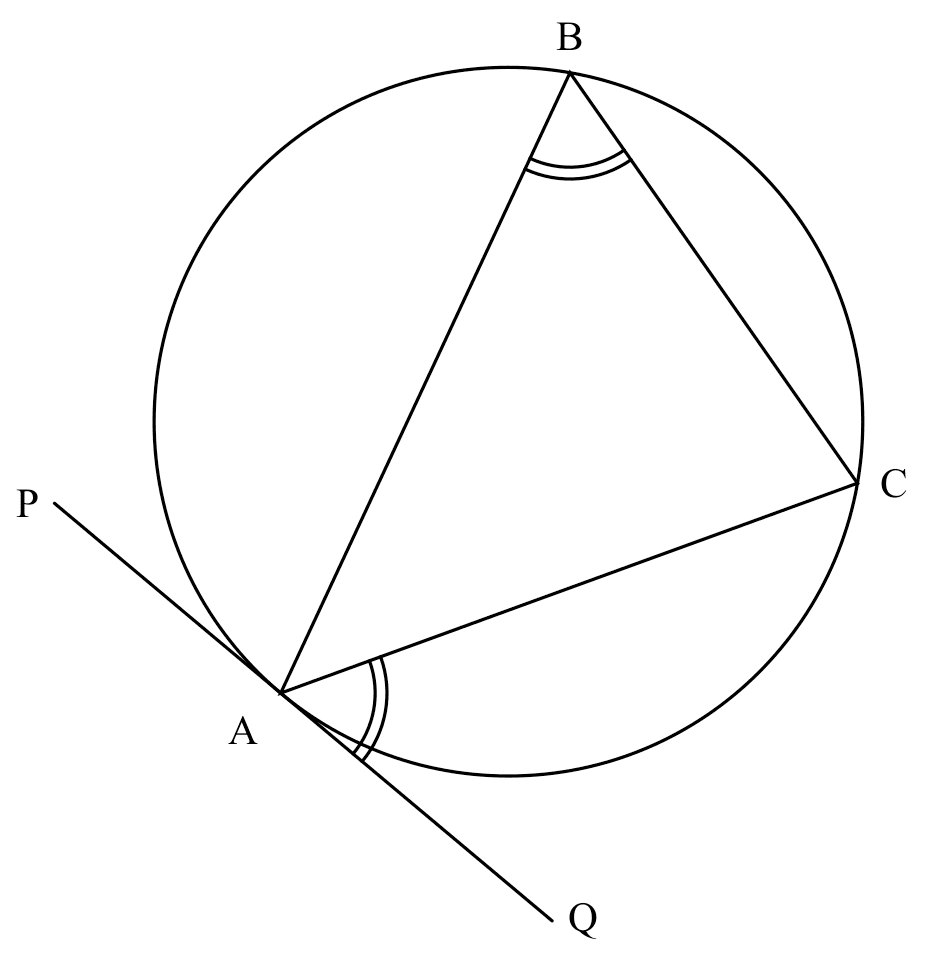
If
If PQ is tangent at A,
Then
$\angle QAC = \angle ABC$
converse of $\angle$s in alt. segment
converse of $\angle$s in alt. segment
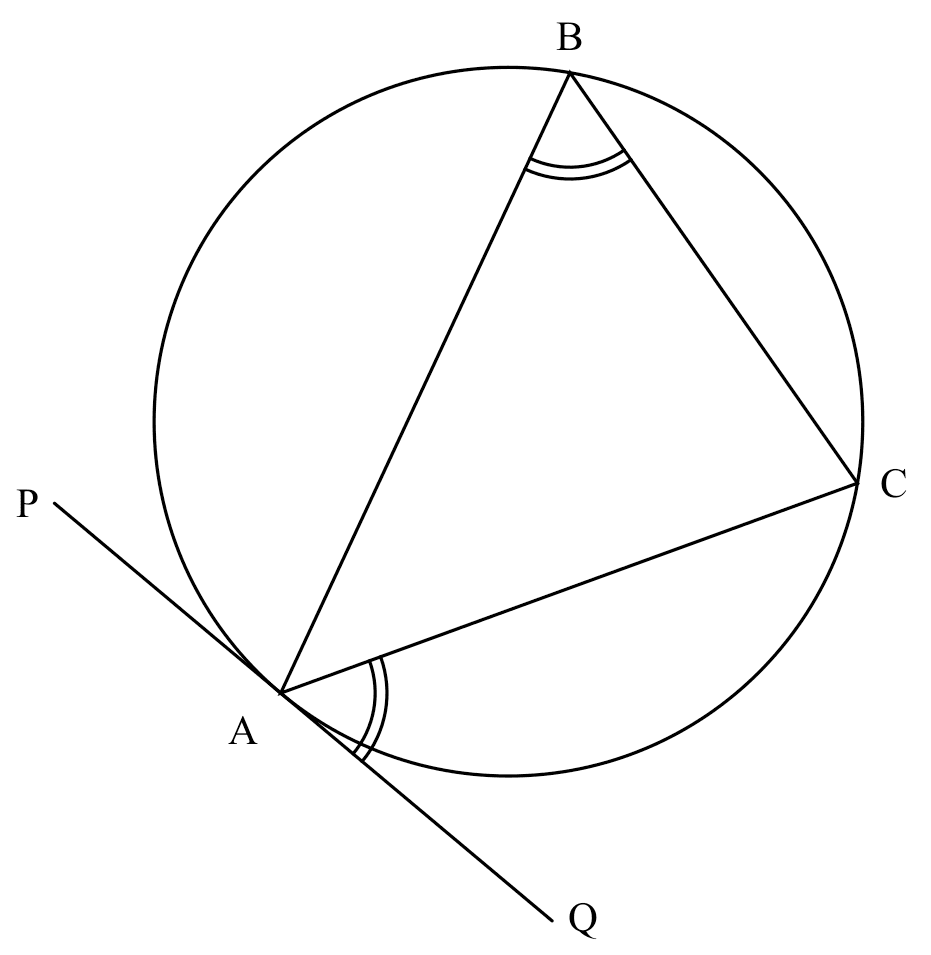
If
If $\angle QAC = \angle ABC$,
Then
$PQ$ is tangent at A